The Tissue Level of Organization
4.0 Introduction
Chapter Targets
After finding out this chapter, it is possible for you to to:
4.1 – Establish the primary tissue sorts and talk about their roles within the human physique.
4.2 – Describe the structural traits of the assorted epithelial tissues and the way these traits allow their features.
4.3 – Describe the structural traits of the assorted connective tissues and the way these traits allow their features.
4.4 – Describe the traits of muscle tissue and the way these dictate muscle operate.
4.5 – Describe the traits of nervous tissue and the way these allow the distinctive features of nervous tissue.
4.6 – Describe the method of tissue response to damage.
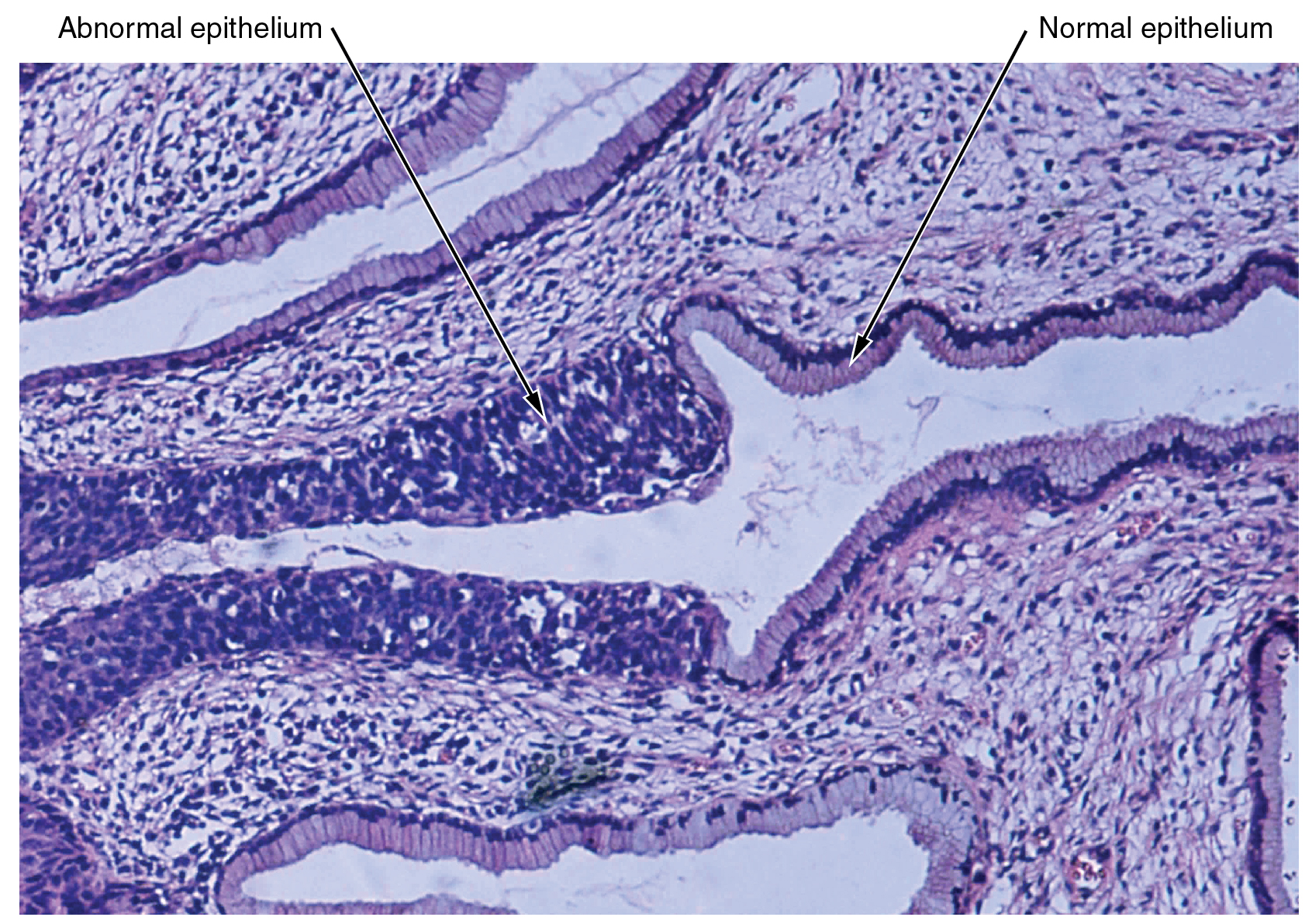
The cells discovered within the human physique comprise basically the identical inside buildings but they range enormously in form and performance. The variation in cells shouldn’t be randomly distributed all through the physique, fairly, they happen in organized layers. Such aggregations of cells which might be related in construction and work collectively to carry out a specialised operate are known as tissues. The micrograph that opens this chapter reveals the excessive diploma of group amongst various kinds of cells within the tissue of the cervix. It’s also possible to see how that group breaks down when most cancers takes over the common mitotic functioning of a cell.
The human physique begins as a single cell at fertilization. As this fertilized egg divides, it offers rise to trillions of cells, every constructed from the identical blueprint, however organizing into tissues and turning into irreversibly dedicated to a developmental pathway.
4.1 Forms of Tissues
Studying Targets
Establish the primary tissue sorts and talk about their roles within the human physique.
By the top of this part, it is possible for you to to:
- Establish the 4 main tissue sorts and talk about the construction and performance of every
- Describe the embryonic origin of tissue
- Establish the assorted forms of tissue membranes and the distinctive qualities of every
The time period tissue is used to explain a gaggle of cells which might be related in construction and carry out a particular operate. Histology is the the sector of examine that entails the microscopic examination of tissue look, group, and performance.
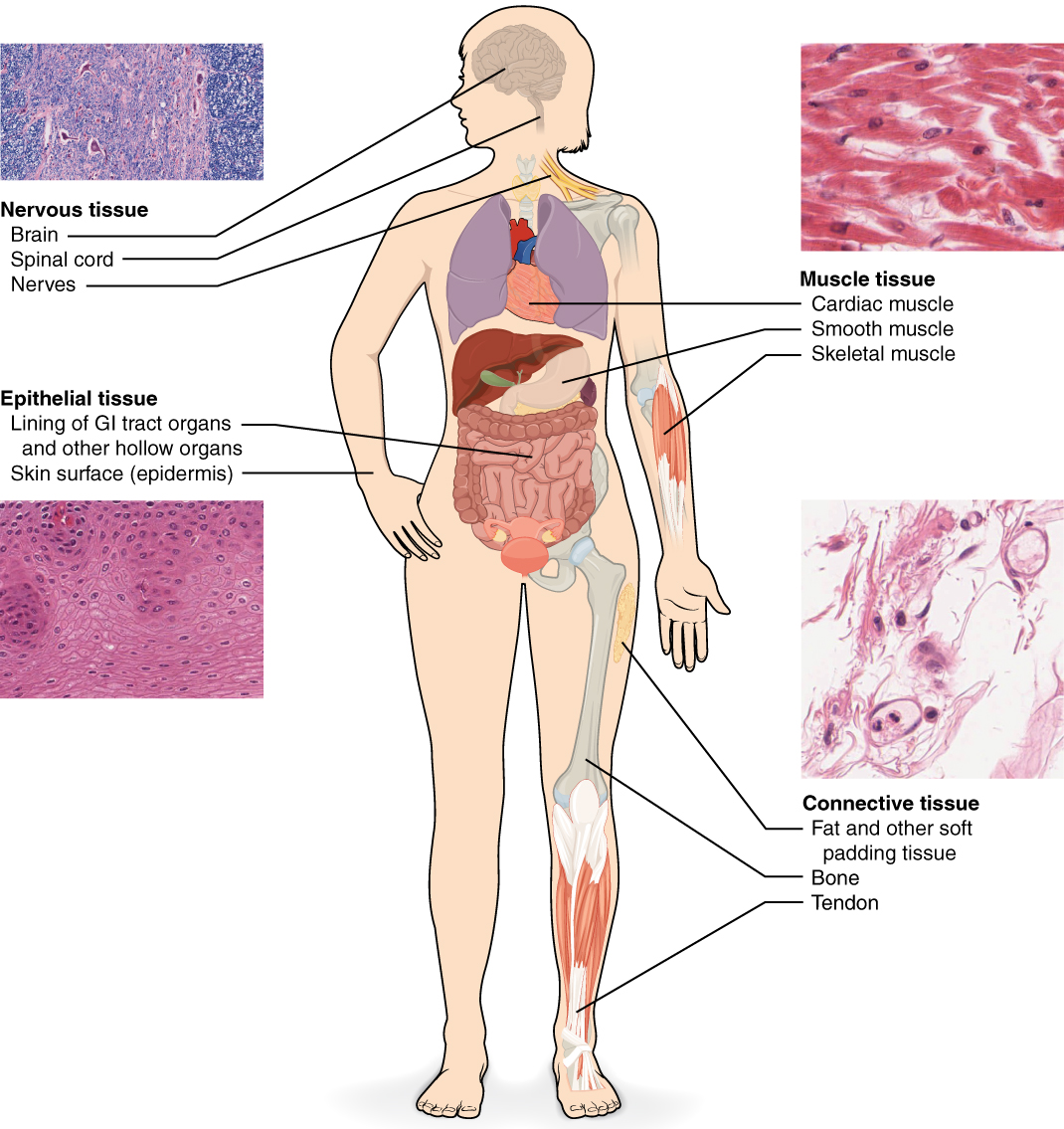
Tissues are organized into 4 broad classes primarily based on structural and useful similarities. These classes are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. The first tissue sorts work collectively to contribute to the general well being and upkeep of the human physique. Thus, any disruption within the construction of a tissue can result in damage or illness.
The 4 Main Tissue Varieties
Epithelial tissue refers to teams of cells that cowl the outside surfaces of the physique, line inside cavities and passageways, and kind sure glands. Connective tissue, as its title implies, binds the cells and organs of the physique collectively. Muscle tissue contracts forcefully when excited, offering motion. Nervous tissue can also be excitable, permitting for the technology and propagation of electrochemical alerts within the type of nerve impulses that talk between totally different areas of the physique (Determine 4.1.1).
An understanding of the assorted main tissue sorts current within the human physique is important for understanding the construction and performance of organs that are composed of two or extra main tissue sorts. This chapter will give attention to inspecting epithelial and connective tissues. Muscle and nervous tissue will probably be mentioned intimately in future chapters.
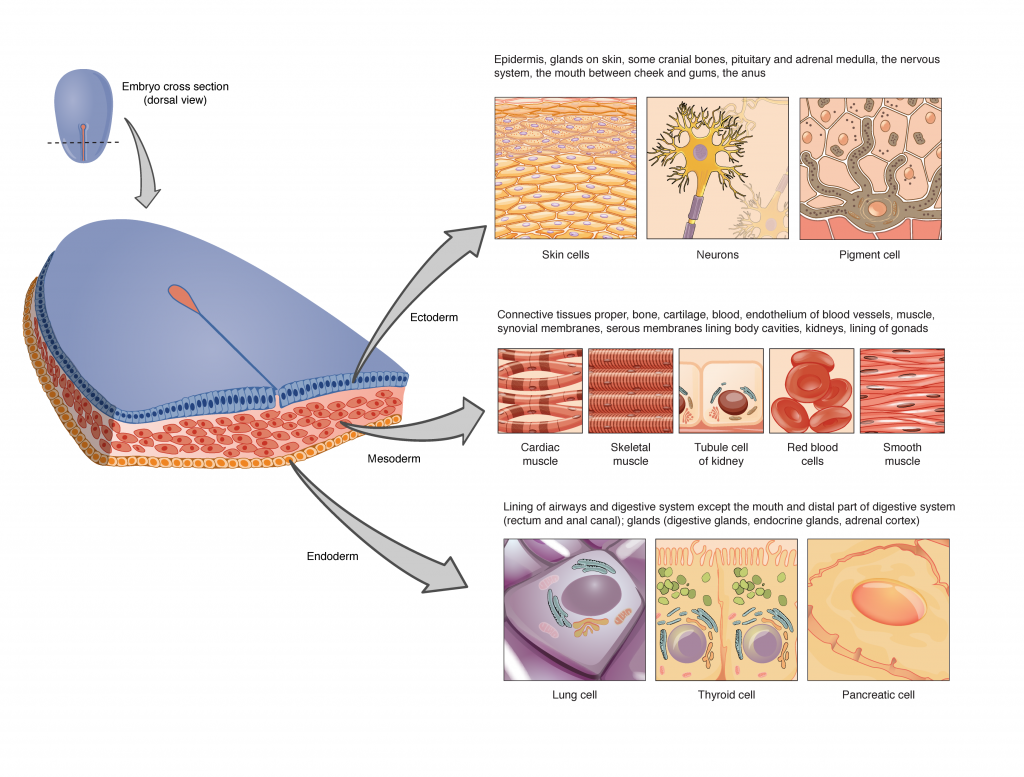
Embryonic Origin of Tissues
The cells composing a tissue share a typical embryonic origin. The zygote, or fertilized egg, is a single cell shaped by the fusion of an egg and sperm cell. After fertilization, the zygote offers rise many cells to kind the embryo. The primary embryonic cells generated have the flexibility to distinguish into any sort of cell within the physique and, as such, are referred to as all-powerful, that means every has the capability to divide, differentiate, and grow to be a brand new organism. As cell proliferation progresses, three main cell strains are established throughout the embryo. Every of those strains of embryonic cells types the distinct germ layers from which all of the tissues and organs of the human physique ultimately kind. Every germ layer is recognized by its relative place: ectoderm (ecto- = “outer”), mesoderm (meso- = “center”), and endoderm (endo- = “internal”). Determine 4.1.2 reveals the forms of tissues and organs related to every of the three germ layers. Be aware that epithelial tissue originates in all three layers, whereas nervous tissue derives primarily from the ectoderm and muscle tissue derives from the mesoderm.
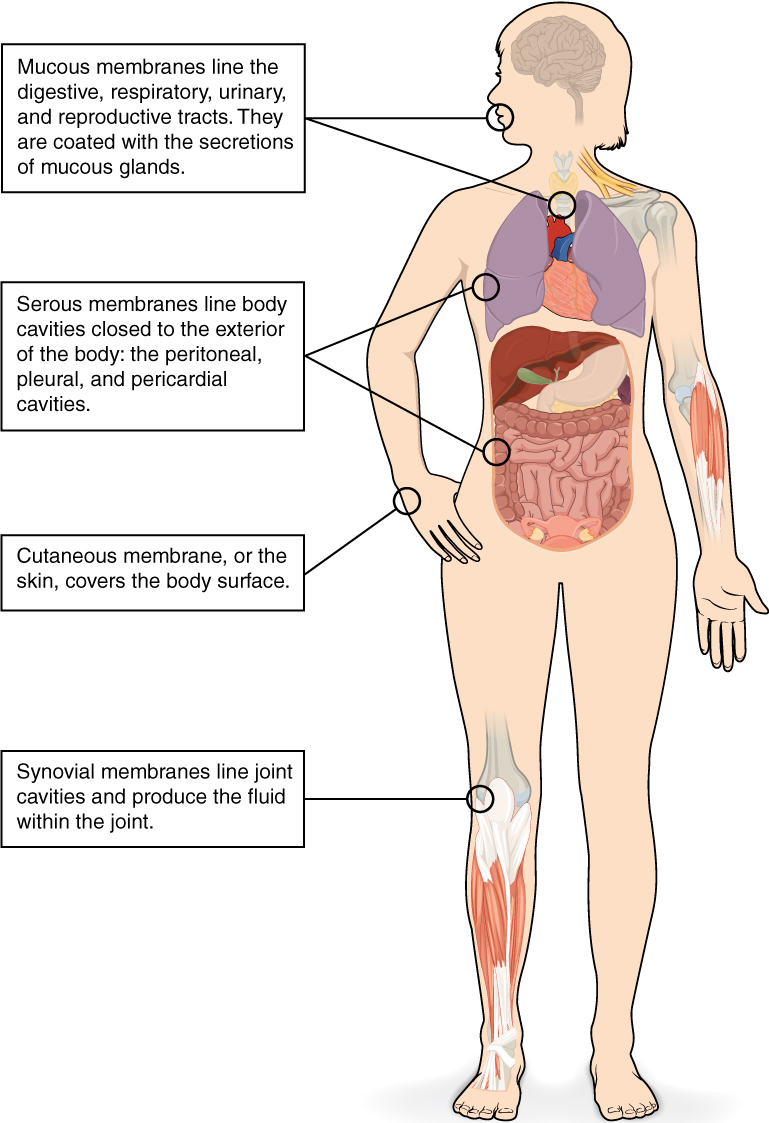
Tissue Membranes
A tissue membrane is a skinny layer or sheet of cells that both covers the skin of the physique (e.g., pores and skin), strains an inside physique cavity (e.g., peritoneal cavity), strains a vessel (e.g., blood vessel), or strains a movable joint cavity (e.g., synovial joint). Two primary forms of tissue membranes are acknowledged primarily based on the first tissue sort composing every: connective tissue membranes and epithelial membranes (Determine 4.1.3).
Connective Tissue Membranes
A connective tissue membrane is constructed completely of connective tissue. The sort of membrane could also be discovered encapsulating an organ, such because the kidney, or lining the cavity of a freely movable joint (e.g., shoulder). When lining a joint, this membrane is known as a synovial membrane. Cells within the internal layer of the synovial membrane launch synovial fluid, a pure lubricant that permits the bones of a joint to maneuver freely in opposition to each other with lowered friction.
Epithelial Membranes
An epithelial membrane consists of an epithelial layer hooked up to a layer of connective tissue. A mucous membrane, typically referred to as a mucosa, strains a physique cavity or hole passageway that’s open to the exterior setting. The sort of membrane may be discovered lining parts of the digestive, respiratory, excretory, and reproductive tracts. Mucus, produced by uniglandular cells and glandular tissue, coats the epithelial layer. The underlying connective tissue, referred to as the lamina propria (actually “personal layer”), helps help the epithelial layer.
A serous membrane strains the cavities of the physique that don’t open to the exterior setting. Serous fluid secreted by the cells of the epithelium lubricates the membrane and reduces abrasion and friction between organs. Serous membranes are recognized based on location. Three serous membranes are discovered lining the thoracic cavity; two membranes that cowl the lungs (pleura) and one membrane that covers the center (pericardium). A fourth serous membrane, the peritoneum, strains the peritoneal cavity, protecting the stomach organs and forming double sheets of mesenteries that droop lots of the digestive organs.
A cutaneous membrane is a multi-layered membrane composed of epithelial and connective tissues. The apical floor of this membrane uncovered to the exterior setting and is roofed with useless, keratinized cells that assist shield the physique from desiccation and pathogens. The pores and skin is an instance of a cutaneous membrane.
Chapter Assessment
Aggregations of cells within the human physique be categorized into 4 forms of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues act as coverings, controlling the motion of supplies throughout their floor. Connective tissue binds the assorted components of the physique collectively, offering help and safety. Muscle tissue permits the physique to maneuver and nervous tissues features in communication.
All cells and tissues within the physique derive from three germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Membranes are layers of connective and epithelial tissues that line the exterior setting and inside physique cavities of the physique. Synovial membranes are connective tissue membranes that shield and line the freely-movable joints. Epithelial membranes are composed of each epithelial tissue and connective tissue. These membranes are discovered lining the exterior physique floor (cutaneous membranes and mucous membranes) or lining the inner physique cavities (serous membranes).
4.2 Epithelial Tissue
Studying Targets
Describe the structural traits of the assorted epithelial tissues and the way these traits allow their features.
By the top of this part, it is possible for you to to:
- Clarify the overall construction and performance of epithelial tissue
- Distinguish between tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and hole junctions
- Distinguish between easy epithelia and stratified epithelia, in addition to between squamous, cuboidal, and columnar epithelia
- Describe the construction and performance of endocrine and exocrine glands
Epithelial tissue primarily seems as massive sheets of cells protecting all surfaces of the physique uncovered to the exterior setting and lining inside physique cavities. As well as, epithelial tissue is chargeable for forming a majority of glandular tissue discovered within the human physique.
Epithelial tissue is derived from all three main embryonic layers. The epithelial tissue composing cutaneous membranes develops from the ectoderm. Epithelial tissue composing a majority of the mucous membranes originate within the endoderm. Epithelial tissue that strains vessels and open areas throughout the physique are derived from mesoderm. Of explicit word, epithelial tissue that strains vessels within the lymphatic and cardiovascular programs known as endothelium whereas epithelial tissue that types the serous membranes lining the true cavities known as mesothelium.
No matter its location and performance, all epithelial tissue shares vital structural options. First, epithelial tissue is very mobile, with little or no extracellular materials current between cells. Second, adjoining cells kind specialised intercellular connections referred to as cell junctions. Third, epithelial cells exhibit polarity with variations in construction and performance between the uncovered, or apical, going through cell floor and the basal floor closest to the underlying tissue. Fourth, epithelial tissues are avascular; vitamins should enter the tissue by diffusion or absorption from underlying tissues or the floor. Final, epithelial tissue is able to quickly changing broken and useless cells, needed with respect to the cruel setting this tissue encounters.
Epithelial Tissue Operate:
Epithelial tissues present the physique’s first line of safety from bodily, chemical, and organic injury. The cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the physique, controlling permeability by permitting selective switch of supplies throughout its floor. All substances that enter the physique should cross an epithelium.
Many epithelial cells are able to secreting mucous and different particular chemical compounds onto their apical surfaces. For instance, the epithelium of the small gut releases digestive enzymes and cells lining the respiratory tract secrete mucous that traps incoming microorganisms and particles.
The Epithelial Cell
Epithelial cells are sometimes characterised by unequal distribution of organelles and membrane-bound proteins between their apical and basal surfaces. Buildings discovered on some epithelial cells are an adaptation to particular features. For instance, cilia are extensions of the apical cell membrane which might be supported by microtubules. These extensions beat in unison, permitting for the motion of fluids and particles alongside the floor. Such ciliated epithelia line the ventricles of the mind the place it helps flow into cerebrospinal fluid and line the respirtatory system the place it helps sweep particles of mud and pathogens up and out of the respiratory tract.
Epithelial cells in shut contact with underlying connective tissues secrete glycoproteins and collagen from their basal floor which types the basal lamina. The basal lamina interacts with the reticular lamina secreted by the underlying connective tissue, forming a basement membrane that helps anchor the layers collectively.
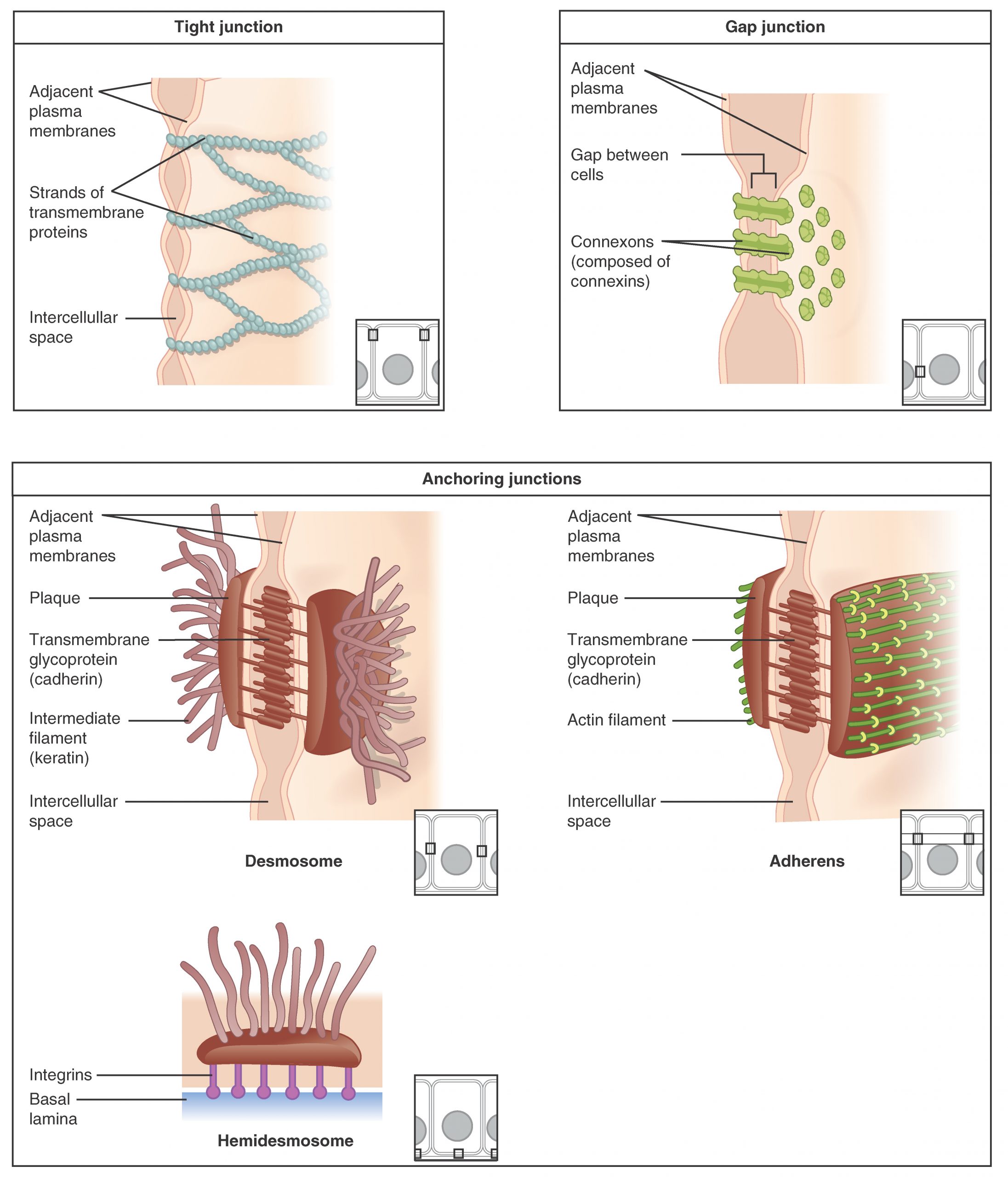
Cells of epithelia are intently linked with restricted extracellular materials current. Three primary forms of connections could also be current: tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and hole junctions (Determine 4.2.1).
Forms of Cell Junctions
Epithelial cells are held shut collectively by cell junctions. The three primary forms of cell-to-cell junctions are tight junctions, hole junctions, and anchoring junctions.
A Tight junction restricts the motion of fluids between adjoining cells because of the presence of integral proteins that fuse collectively to kind a agency seal. Tight junctions are noticed within the epithelium of the urinary bladder, stopping the escape of fluids comprising the urine.
An anchoring junction offers a robust but versatile connection between epithelial cells. There are three forms of anchoring junctions: desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and adherens. Desmosomes maintain neighboring cells collectively by means of cadherin molecules that are embedded in protein plates within the cell membranes and hyperlink collectively between the adjoining cells. Hemidesmosomes, which appear like half a desmosome, hyperlink cells to elements within the extracellular matrix, such because the basal lamina. Whereas related in look to desmosomes, hemidesmosomes use adhesion proteins referred to as integrins fairly than cadherins. Adherens use both cadherins or integrins relying on whether or not they’re linking to different cells or matrix. These junctions are characterised by the presence of the contractile protein actin positioned on the cytoplasmic floor of the cell membrane. These junctions affect the form and folding of the epithelial tissue.
In distinction with the tight and anchoring junctions, a hole junction types an intercellular passageway between the membranes of adjoining cells to facilitate the motion of small molecules and ions between cells. These junctions thus enable electrical and metabolic coupling of adjoining cells.
Classification of Epithelial Tissues
Epithelial tissues are categorized based on the form of the cells composing the tissue and by the variety of cell layers current within the tissue.(Determine 4.2.2) Cell shapes are categorized as being both squamous (flattened and skinny), cuboidal (boxy, as vast as it’s tall), or columnar (rectangular, taller than it’s vast). Equally, cells within the tissue may be organized in a single layer, which known as easy epithelium, or multiple layer, which known as stratified epithelium. Pseudostratified (pseudo- = “false”) describes an epithelial tissue with a single layer of irregularly formed cells that give the looks of multiple layer. Transitional describes a type of specialised stratified epithelium through which the form of the cells, and the variety of layers current, can range relying on the diploma of stretch inside a tissue.
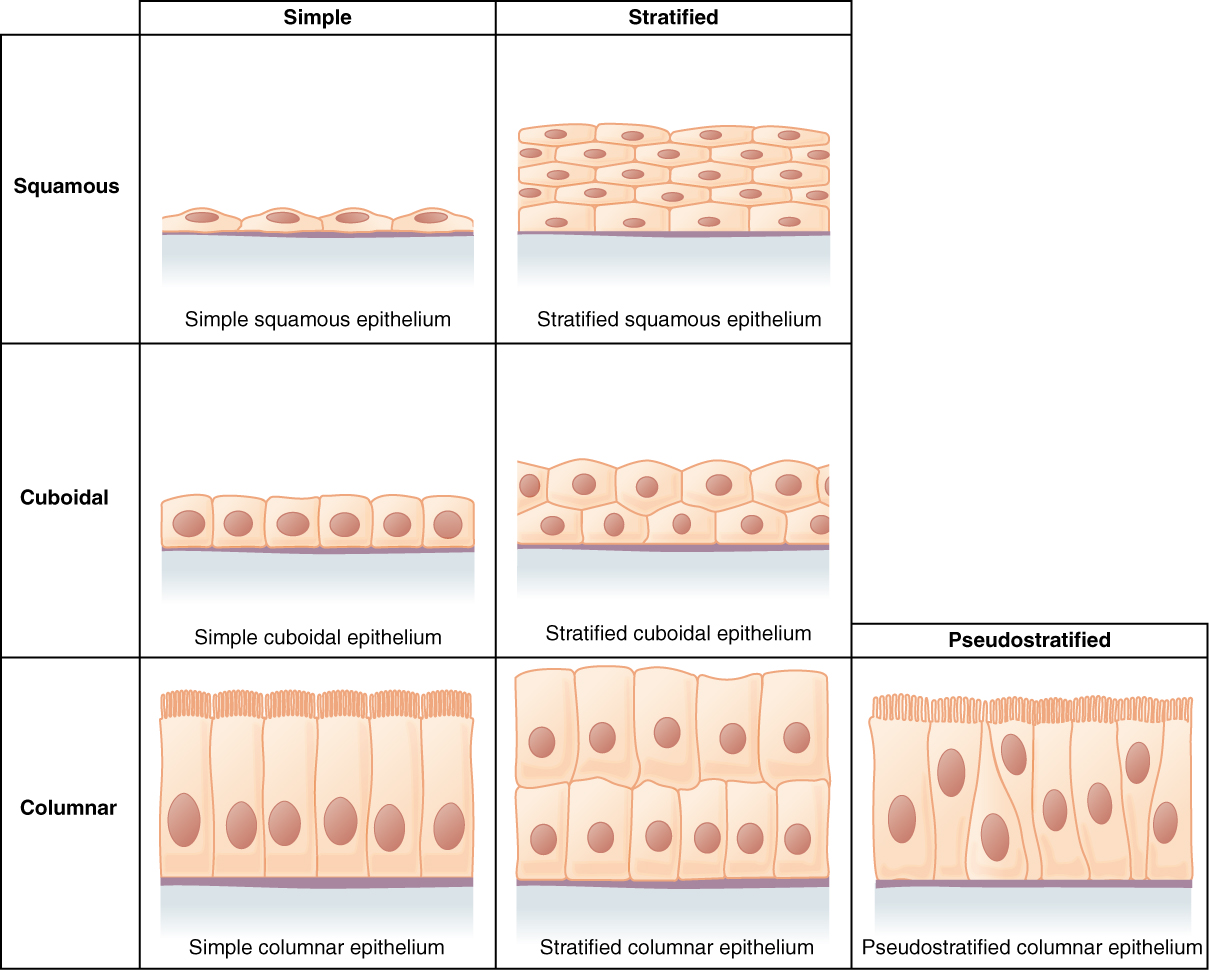
Epithelial tissue is classed primarily based on the form of the cells current and the variety of cell layers current. Determine 4.2.2 summarizes the totally different classes of epithelial cell tissue cells.
Exterior Web site
Abstract of Epithelial Tissue Cells
Watch this video to seek out out extra concerning the anatomy of epithelial tissues. The place within the physique would one discover non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium?
Easy Epithelium
The cells in a easy squamous epithelium have the looks of skinny scales. The nuclei of squamous cells have a tendency to look flat, horizontal, and elliptical, mirroring the type of the cell. Easy squamous epithelium, due to the thinness of the cells, is current the place fast passage of chemical compounds is critical corresponding to the liner of capillaries and the small air sacs of the lung. This epithelial sort can also be discovered composing the mesothelium which secretes serous fluid to lubricate the inner physique cavities.
In easy cuboidal epithelium, the nucleus of the box-like cells seems spherical and is mostly positioned close to the middle of the cell. These epithelia are concerned within the secretion and absorptions of molecules requiring energetic transport. Easy cuboidal epithelia are noticed within the lining of the kidney tubules and within the ducts of glands.
In easy columnar epithelium, the nucleus of the tall column-like cells tends to be elongated and positioned within the basal finish of the cells. Just like the cuboidal epithelia, this epithelium is energetic within the absorption and secretion of molecules utilizing energetic transport. Easy columnar epithelium types a majority of the digestive tract and a few components of the feminine reproductive tract. Ciliated columnar epithelium consists of straightforward columnar epithelial cells with cilia on their apical surfaces. These epithelial cells are discovered within the lining of the fallopian tubes the place the help within the passage of the egg, and components of the respiratory system, the place the beating of the cilia helps take away particulate matter.
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a kind of epithelium that seems to be stratified however as a substitute consists of a single layer of irregularly formed and otherwise sized columnar cells. In pseudostratified epithelium, nuclei of neighboring cells seem at totally different ranges fairly than clustered within the basal finish. The association offers the looks of stratification, however in actual fact, all of the cells are involved with the basal lamina, though some don’t attain the apical floor. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is discovered within the respiratory tract, the place a few of these cells have cilia.
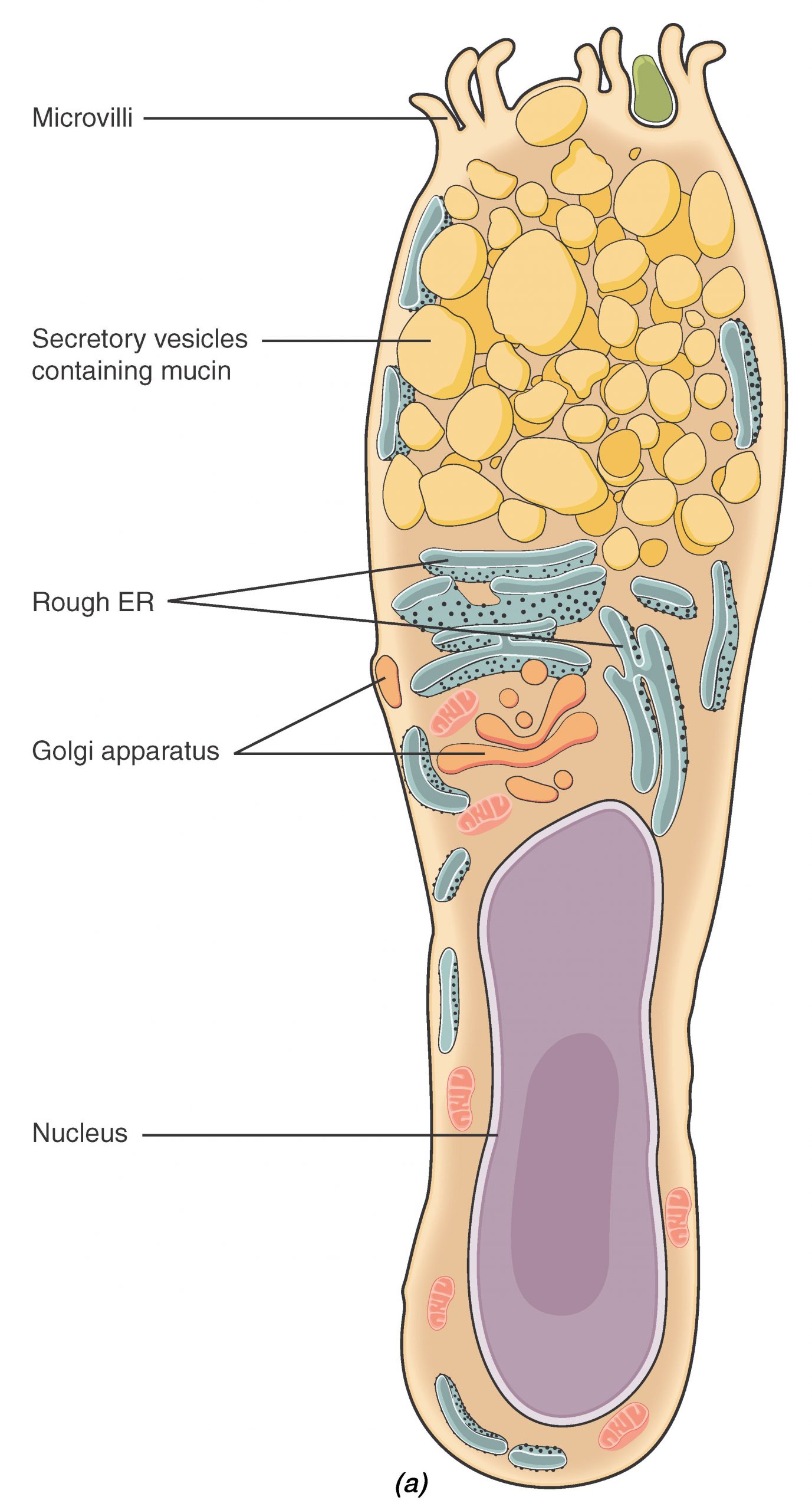
Each easy and pseudostratified columnar epithelia are heterogeneous epithelia as a result of they embody further forms of cells interspersed among the many epithelial cells. For instance, a goblet cell is a mucous-secreting unicellular gland interspersed between the columnar epithelial cells of a mucous membrane (Determine 4.2.3).
Stratified Epithelium
A stratified epithelium consists of a number of stacked layers of cells. This epithelium protects in opposition to bodily and chemical injury. The stratified epithelium is called by the form of probably the most apical layer of cells, closest to the free house.
Stratified squamous epithelium is the most typical sort of stratified epithelium within the human physique. The apical cells seem squamous, whereas the basal layer accommodates both columnar or cuboidal cells. The highest layer could also be coated with useless cells containing keratin. The pores and skin is an instance of a keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. Alternatively, the liner of the oral cavity is an instance of an unkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. Stratified cuboidal epithelium and stratified columnar epithelium may also be present in sure glands and ducts, however are comparatively uncommon within the human physique.
One other sort of stratified epithelium is transitional epithelium, so-called due to the gradual adjustments within the shapes and layering of the cells because the epithelium lining the increasing hole organ is stretched. Transitional epithelium is discovered solely within the urinary system, particularly the ureters and urinary bladder. When the bladder is empty, this epithelium is convoluted and has cuboidal-shaped apical cells with convex, umbrella formed, surfaces. Because the bladder fills with urine, this epithelium loses its convolutions and the apical cells transition in look from cuboidal to squamous. It seems thicker and extra multi-layered when the bladder is empty, and extra stretched out and fewer stratified when the bladder is full and distended.
Glandular Epithelium
A gland is a construction made up of a number of cells modified to synthesize and secrete chemical substances. Most glands include teams of epithelial cells. A gland may be categorized as an endocrine gland, a ductless gland that releases secretions instantly into surrounding tissues and fluids (endo- = “inside”), or an exocrine gland whose secretions go away by way of a duct that opens to the exterior setting (exo- = “outdoors”).
Endocrine Glands
The secretions of endocrine glands are referred to as hormones. Hormones are launched into the interstitial fluid, diffuse into the bloodstream, and are delivered to cells which have receptors to bind the hormones. The endocrine system a significant communication system coordinating the regulation and integration of physique responses. These glands will probably be mentioned in a lot larger element in a later chapter.
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands launch their contents by way of a duct or duct system that in the end results in the exterior setting. Mucous, sweat, saliva, and breast milk are all examples of secretions launched by exocrine glands.
Glandular Construction
Exocrine glands are categorized as both unicellular or multicellular. Unicellular glands are particular person cells that are scattered all through an epithelial lining. Goblet cells are an instance of a unicellular gland sort discovered extensively within the mucous membranes of the small and huge gut.
Multicellular exocrine glands are composed of two or extra cells which both secrete their contents instantly into an internal physique cavity (e.g., serous glands), or launch their contents right into a duct. If there’s a single duct carrying the contents to the exterior setting then the gland is known as a easy gland. Multicellular glands which have ducts divided into a number of branches known as a compound gland (Figure 4.2.4). Along with the variety of ducts current, multicellular glands are additionally categorized primarily based on the form of the secretory portion of the gland. Tubular glands have enlongated secretory areas (much like a check tube in form) whereas alveolar (acinar) glands have a secretory area that’s spherical in form. Mixtures of the 2 secretory areas are often called tubuloalveolar (tubuloacinar) glands.
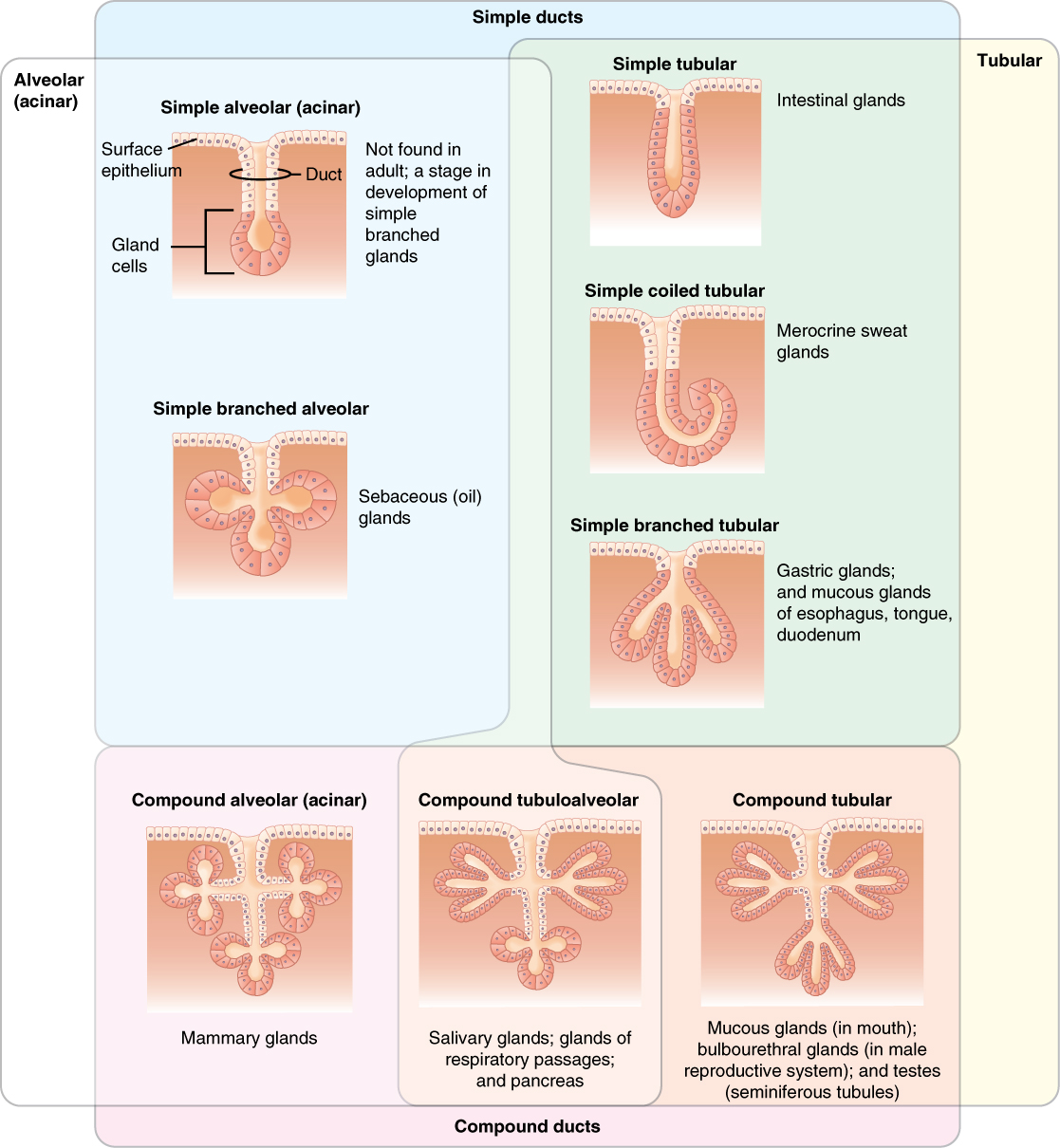
Exocrine glands are categorized by the association of ducts emptying the gland and the form of the secretory area.
Strategies and Forms of Secretion
Along with the glandular construction, exocrine glands may be categorized by their mode of secretion and the character of the substances launched (Determine 4.2.5). Merocrine secretion is the most typical sort of exocrine secretion. The secretions are enclosed in vesicles that transfer to the apical floor of the cell the place the contents are launched by exocytosis. For instance, saliva containing the glycoprotein mucin is a merocrine secretion. The glands that produce and secrete sweat are one other instance of merocrine secretion.
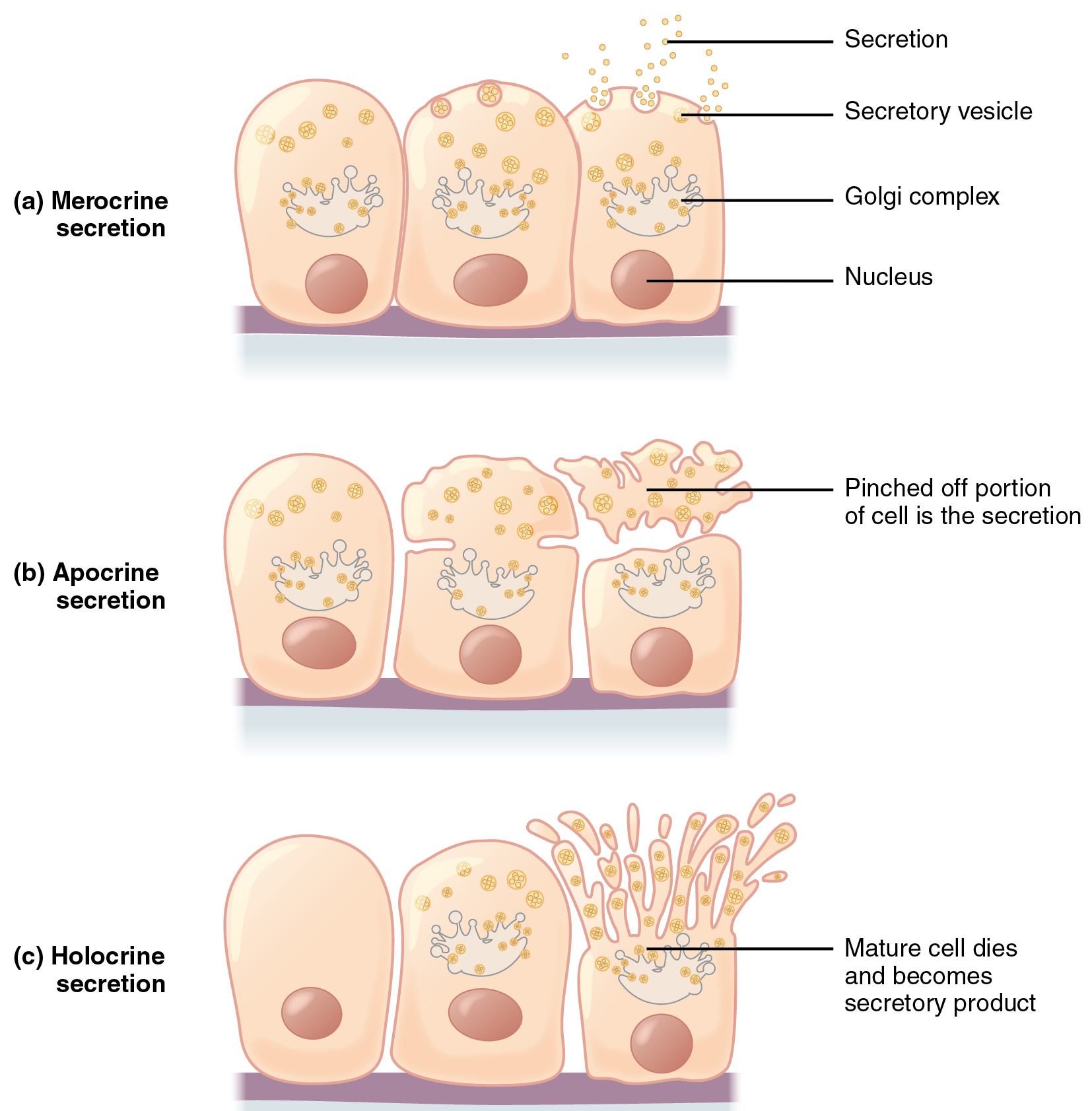
Apocrine secretion happens when secretions accumulate close to the apical portion of a secretory cell. That portion of the cell and its secretory contents pinch off from the cell and are launched. The sweat glands of the armpit are categorized as apocrine glands. Like merocrine glands, apocrine glands proceed to supply and secrete their contents with little injury brought about to the cell as a result of the nucleus and golgi areas stay intact after the secretory occasion.
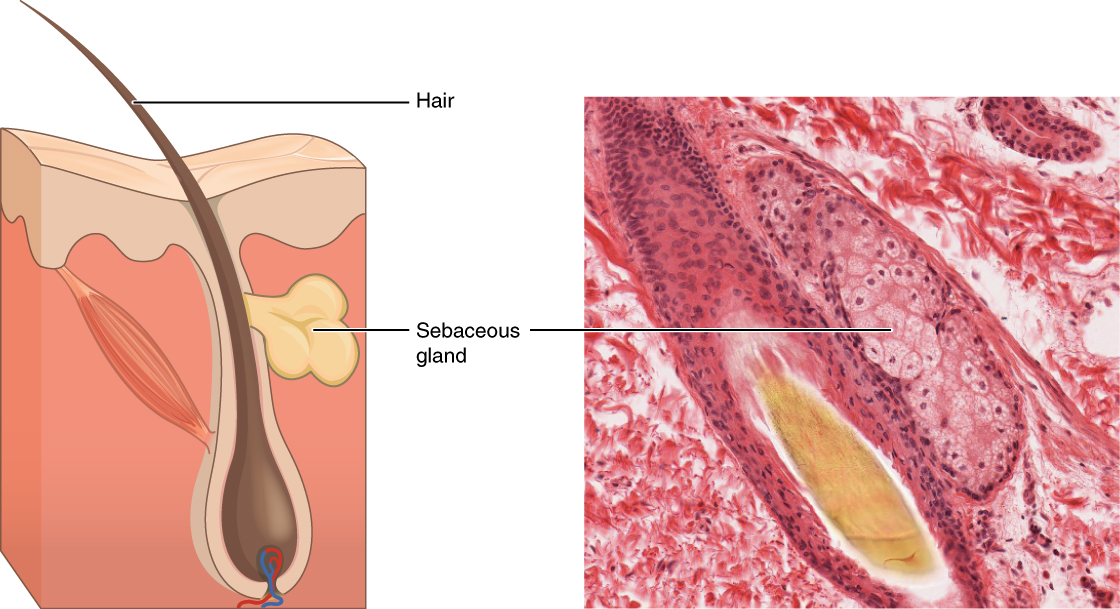
In distinction, the method of holocrine secretion entails the rupture and destruction of the whole gland cell. The cell accumulates its secretory merchandise and releases them solely when the cell bursts. New gland cells differentiate from cells within the surrounding tissue to exchange these misplaced by secretion. The sebaceous glands that produce the oils on the pores and skin and hair are an instance of a holocrine glands (Determine 4.2.6).
Glands are additionally named primarily based on the merchandise they produce. A serous gland produces watery, blood-plasma-like secretions wealthy in enzymes, whereas a mucous gland releases a extra viscous product wealthy within the glycoprotein mucin. Each serous and mucous secretions are widespread within the salivary glands of the digestive system. Such glands releasing each serous and mucous secretions are sometimes called seromucous glands.
Chapter Assessment
In epithelial tissue, cells are intently full of little or no extracellular matrix apart from the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from underlying tissue. The primary features of epithelia are safety from the setting, protection, secretion and excretion, absorption, and filtration. Cells are certain collectively by tight junctions that kind an impermeable barrier. They may also be linked by hole junctions, which permit free change of soluble molecules between cells, and anchoring junctions, which connect cell to cell or cell to matrix. The various kinds of epithelial tissues are characterised by their mobile shapes and preparations: squamous, cuboidal, or columnar epithelia. Single cell layers kind easy epithelia, whereas stacked cells kind stratified epithelia. Only a few capillaries penetrate these tissues.
Glands are secretory tissues and organs which might be derived from epithelial tissues. Exocrine glands launch their merchandise by way of ducts. Endocrine glands secrete hormones instantly into the interstitial fluid and blood stream. Glands are categorized each based on the kind of secretion and by their construction. Merocrine glands secrete merchandise as they’re synthesized. Apocrine glands launch secretions by pinching off the apical portion of the cell, whereas holocrine gland cells retailer their secretions till they rupture and launch their contents. On this case, the cell turns into a part of the secretion.
4.3 Connective Tissue Helps and Protects
Studying Targets
Describe the structural traits of the assorted connective tissues and the way these traits allow their features.
By the top of this part, it is possible for you to to:
- Establish and distinguish between the totally different sort of connective tissue: correct, supportive, and fluid – and affiliate every with their operate and site
- Describe the widespread structural components of connective tissue
- Describe how the structural properties of connective tissue relate to the distinctive features of the tissue
Features of Connective Tissues
Connective tissues carry out many features within the physique, most significantly, they help and join different tissues: from the connective tissue sheath that surrounds a muscle, to the tendons that connect muscle tissues to bones, and to the skeleton that helps the positions of the physique. Safety is one other main operate of connective tissue, within the type of fibrous capsules and bones that shield delicate organs. Specialised cells in connective tissue defend the physique from microorganisms that enter the physique. Transport of gases, vitamins, waste, and chemical messengers is ensured by specialised fluid connective tissues, corresponding to blood and lymph. Adipose cells retailer surplus vitality within the type of fats and contribute to the thermal insulation of the physique.
Embryonic Connective Tissue
All connective tissues derive from the mesodermal layer of the embryo (see Figure 4.2.2). The primary connective tissue to develop within the embryo is mesenchyme, the stem cell line from which all connective tissues are later derived. Clusters of mesenchymal cells are scattered all through grownup tissue and provide the cells wanted for alternative and restore after a connective tissue damage. A second sort of embryonic connective tissue types within the umbilical wire, referred to as mucous connective tissue or Wharton’s jelly. This tissue is not current after start, leaving solely scattered mesenchymal cells all through the physique.
Structural Components of Connective Tissue
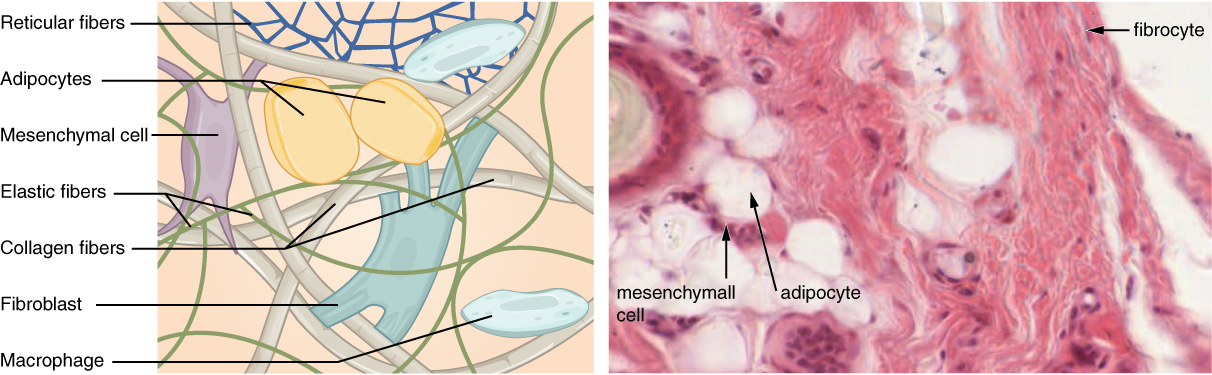
Connective tissues are available in an enormous number of types, but they sometimes have in widespread three attribute elements: cells, massive quantities of amorphous floor substance, and protein fibers. Not like epithelial tissue, which consists of cells intently packed collectively, cells of connective tissue are extra broadly dispersed inside an extracellular matrix (ECM). The matrix performs a significant function within the functioning of this tissue. The foremost element of the matrix is floor substance. This floor substance is often a fluid, but it surely may also be mineralized and stable, as in bones. The quantity and construction of every element correlates with the operate of the tissue, from the inflexible floor substance in bones supporting the physique to the inclusion of specialised cells; for instance, a phagocytic cell that engulfs pathogens and in addition rids tissue of mobile particles.
Cell Varieties
Every class of connective tissue is shaped by basic cell sorts. The cells may be present in each an energetic kind (suffix –blast), the place they’re dividing and secreting the elements of floor substance, and an in-active kind (suffix –cyte). Essentially the most ample cell in connective tissue correct is the fibroblast. Polysaccharides and proteins secreted by fibroblasts mix with extra-cellular fluids to supply a viscous floor substance that, with embedded fibrous proteins and cells, types the extra-cellular matrix. Chondroblasts and osteoblasts are the first specialised cell sort positioned in cartilage and bone, respectively.
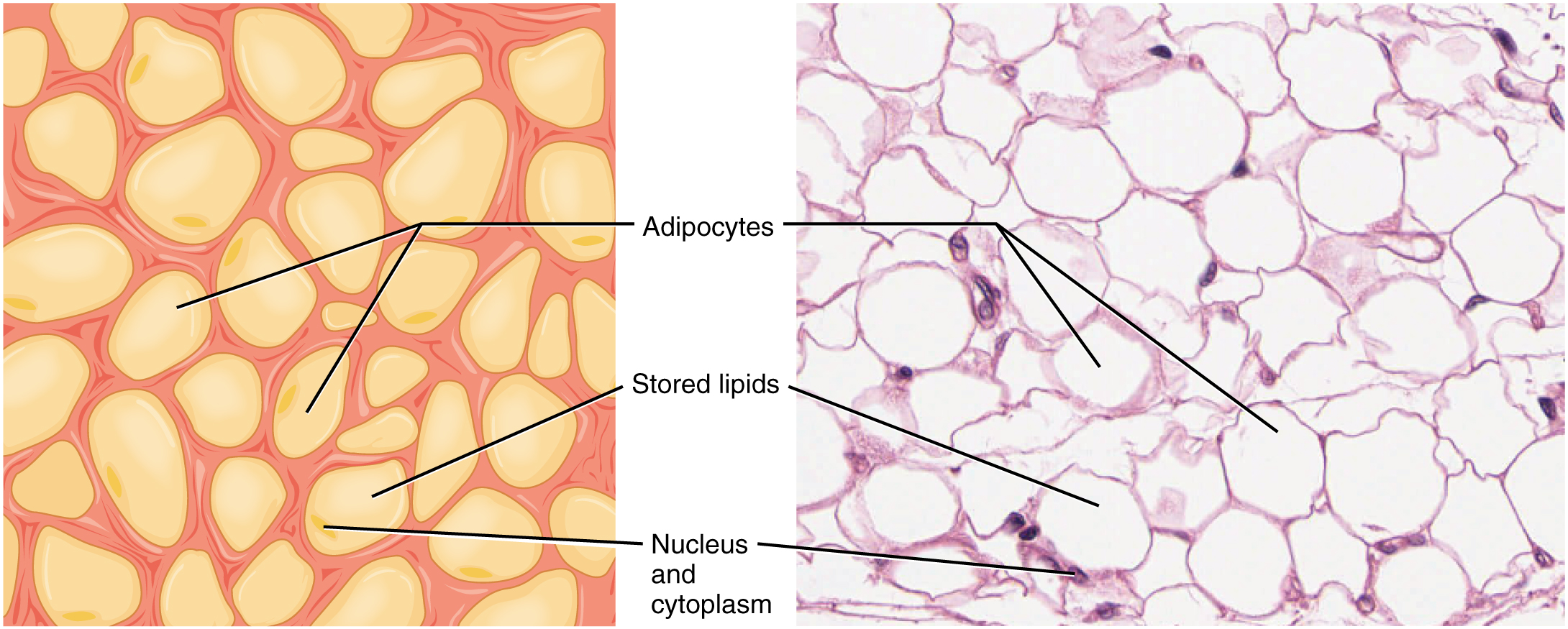
Adipocytes are cells that retailer lipids as droplets that fill many of the cytoplasm. There are two primary forms of adipocytes: white and brown. The brown adipocytes retailer lipids as many droplets, and have excessive metabolic exercise. In distinction, white fats adipocytes retailer lipids as a single massive drop and are metabolically much less energetic. Their effectiveness at storing massive quantities of fats is witnessed in overweight people. The quantity and kind of adipocytes relies on the tissue and site, and range amongst people within the inhabitants.
The mesenchymal cell is a multipotent grownup stem cell. These cells can differentiate into any sort of connective tissue cells wanted for restore and therapeutic of broken tissue.
The macrophage cell is a big cell derived from a monocyte, a kind of blood cell, which enters the connective tissue matrix from the blood vessels. The macrophage cells are a vital part of the immune system, which is the physique’s protection in opposition to potential pathogens and degraded host cells. When stimulated, macrophages launch cytokines, small proteins that act as chemical messengers. Cytokines recruit different cells of the immune system to contaminated websites and stimulate their actions. Roaming, or free, macrophages transfer quickly by amoeboid motion, engulfing infectious brokers and mobile particles. In distinction, mounted macrophages are everlasting residents of their tissues.
The mast cell, present in connective tissue correct, has many cytoplasmic granules. These granules comprise the chemical alerts histamine and heparin. When irritated or broken, mast cells launch histamine, an inflammatory mediator, which causes vasodilation and elevated blood circulation at a website of damage or an infection, together with itching, swelling, and redness (in individuals with mild pores and skin), acknowledged as an allergic response. Mast cells are derived from hematopoietic stem cells and are a part of the immune system.
Connective Tissue Fibers and Floor Substance
Three essential forms of fibers are secreted by fibroblasts: collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers. Collagen fiber is constructed from fibrous protein subunits linked collectively to kind an extended, straight fiber. Collagen fibers, whereas versatile, have nice tensile power, resist stretching, and provides ligaments and tendons their attribute resilience.
An elastic fiber accommodates the protein elastin together with lesser quantities of different proteins and glycoproteins. The primary property of elastin is that after being stretched or compressed, it’ll return to its authentic form. Elastic fibers are distinguished in elastic tissues present in pores and skin, the partitions of huge blood vessels, and in a number of ligaments which help the backbone.
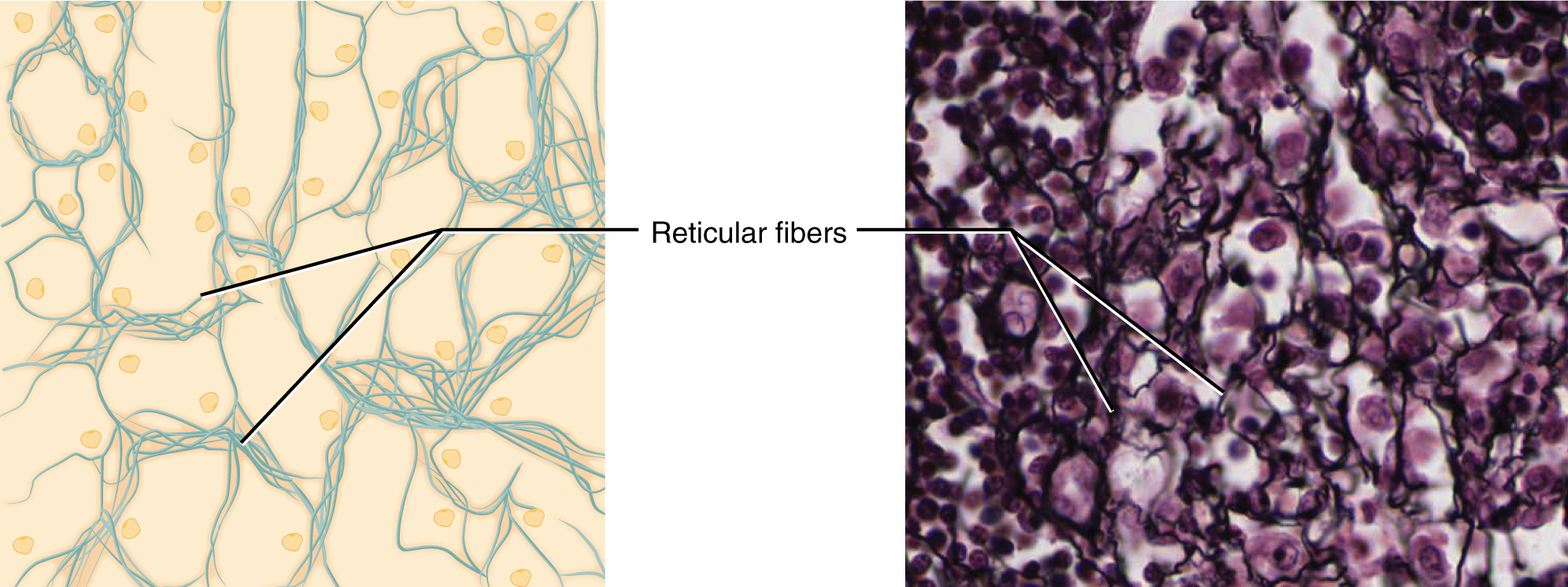
A reticular fiber is shaped from the identical protein subunits as collagen fibers, nonetheless, these fibers stay slender and are organized in a branching community. They’re discovered all through the physique, however are most ample within the reticular tissue of soppy organs, such because the liver and spleen, the place they anchor and supply structural help to the parenchyma (the useful cells, blood vessels, and nerves of the organ).
All of those fiber sorts are embedded in floor substance. Secreted by fibroblasts, floor substance is made from polysaccharides, particularly hyaluronic acid, and proteins. These mix to kind a proteoglycan with a protein core and polysaccharide branches. The proteoglycan attracts and traps obtainable moisture forming the clear, viscous, colorless floor substance.
Classification of Connective Tissues
The three broad classes of connective tissue are categorized based on the traits of their floor substance and the forms of fibers discovered throughout the matrix (Desk 4.1). Connective tissue correct consists of unfastened connective tissue and dense connective tissue. Each tissues have quite a lot of cell sorts and protein fibers suspended in a viscous floor substance. Dense connective tissue is strengthened by bundles of fibers that present tensile power, elasticity, and safety. In unfastened connective tissue, the fibers are loosely organized, leaving massive areas in between. Supportive connective tissue—bone and cartilage—present construction and power to the physique and shield gentle tissues. A couple of distinct cell sorts and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. In bone, the matrix is inflexible and described as calcified due to the deposited calcium salts. In fluid connective tissue, lymph and blood, varied specialised cells flow into in a watery fluid containing salts, vitamins, and dissolved proteins.
| Connective tissue correct | Supportive connective tissue | Fluid connective tissue |
| Free connective tissue: Areolar Adipose Reticular | Cartilage:HyalineFibrocartilageElastic | Blood |
| Dense connective tissue: Common Irregular Elastic | Bone: Compact bone Spongy bone | Lymph |
Connective Tissue Correct
Fibroblasts are current in all connective tissue correct (Determine 4.3.1). Fibrocytes, adipocytes, and mesenchymal cells are mounted cells, which suggests they continue to be throughout the connective tissue. Different cells transfer out and in of the connective tissue in response to chemical alerts. Macrophages, mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and phagocytic cells are present in connective tissue correct however are literally a part of the immune system defending the physique.
Free Connective Tissue
Free connective tissue is discovered between many organs the place it acts each to soak up shock and bind tissues collectively. It permits water, salts, and varied vitamins to diffuse by way of to adjoining or imbedded cells and tissues.
Adipose tissue consists largely of fats storage cells, with little extracellular matrix (Determine 4.3.2). Numerous capillaries enable fast storage and mobilization of lipid molecules. White adipose tissue is most ample. It will possibly seem yellow and owes its colour to carotene and associated pigments from plant meals. White fats contributes largely to lipid storage and might function insulation from chilly temperatures and mechanical accidents. White adipose tissue may be discovered defending the kidneys, cushioning the again of the attention, throughout the stomach, and within the hypodermis. Brown adipose tissue is extra widespread in infants, therefore the time period “child fats.” In adults, there’s a lowered quantity of brown fats and it’s discovered primarily within the neck and clavicular areas of the physique. The numerous mitochondria within the cytoplasm of brown adipose tissue assist clarify its effectivity at metabolizing saved fats. Brown adipose tissue is thermogenic, that means that because it breaks down fat, it releases metabolic warmth, fairly than producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a key molecule utilized in metabolism.
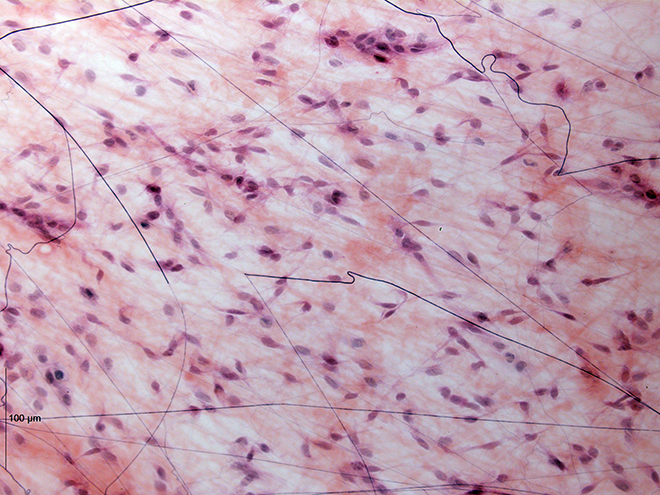
Areolar tissue reveals comparatively little specialization and is probably the most broadly distributed connective tissue within the physique. It accommodates all of the cell sorts and fibers beforehand described and is structured in an apparently random, web-like vogue. It fills the areas between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph vessels, and helps organs within the stomach cavity. Areolar tissue underlies most epithelia and represents the connective tissue element of epithelial membranes.
Reticular tissue is a mesh-like, supportive framework for gentle organs corresponding to lymphatic tissue, the spleen, and the liver (Determine 4.3.3). The reticular fibers kind the community onto which different cells connect. It derives its title from the Latin reticulus, which suggests “little internet.”
Dense Connective Tissue
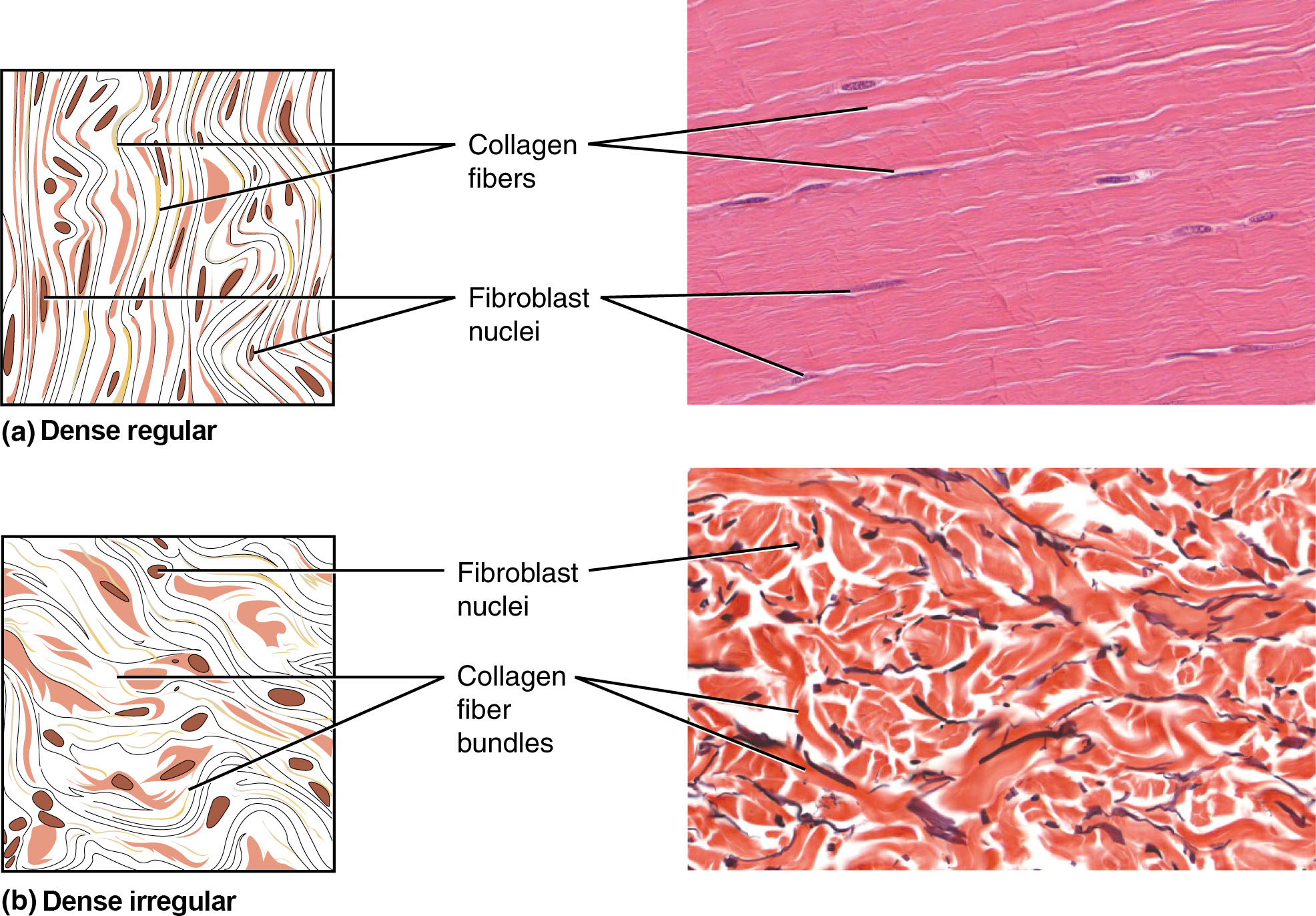
Dense connective tissue accommodates extra collagen fibers than does unfastened connective tissue. As a consequence, it shows larger resistance to stretching and the next tensile power. There are three main classes of dense connective tissue: common, irregular, and elastic. Dense common connective tissue fibers are parallel to one another, enhancing tensile power and resistance to stretching within the route of the fiber orientations. Ligaments and tendons are largely shaped from dense common connective tissue.
In dense irregular connective tissue, the association of proteins fibers is irregular and lacks the uniformity seen in dense common . This association offers the tissue larger power in all instructions and fewer power in anybody explicit route. In some tissues, fibers crisscross and kind a mesh. In different tissues, stretching in a number of instructions is achieved by alternating layers the place fibers run in the identical orientation in every layer, and it’s the layers themselves which might be stacked at an angle. The dermis of the pores and skin is an instance of dense irregular connective tissue wealthy in collagen fibers.
Dense elastic tissue accommodates elastin fibers along with collagen fibers, which permits the tissue to return to its authentic size after stretching. Dense elastic tissues give arterial partitions the power and the flexibility to regain authentic form after stretching (dense CT determine).
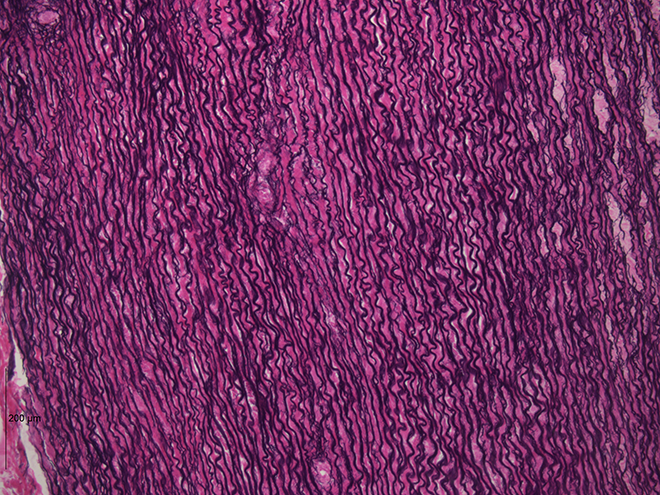
Problems of the Connective Tissue: Tendinitis
Your opponent stands prepared as you put together to hit the serve, however you’re assured that you’ll smash the ball previous your opponent. As you toss the ball excessive within the air, a burning ache shoots throughout your wrist and also you drop the tennis racket. That boring ache within the wrist that you just ignored by way of the summer time is now an insufferable ache. The sport is over for now.
After inspecting your swollen wrist, the physician within the emergency room publicizes that you’ve developed wrist tendinitis. She recommends icing the tender space, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory treatment to ease the ache and to scale back swelling, and full relaxation for a number of weeks. She interrupts your protests that you just can not cease taking part in. She points a stern warning concerning the threat of aggravating the situation and the opportunity of surgical procedure. She consoles you by mentioning that well-known tennis gamers corresponding to Venus and Serena Williams and Rafael Nadal have additionally suffered from tendinitis associated accidents.
What’s tendinitis and the way did it occur? Tendinitis is the irritation of a tendon, the thick band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The situation causes ache and tenderness within the space round a joint. Most frequently, the situation outcomes from repetitive motions over time that pressure the tendons wanted to carry out the duties.
Individuals whose jobs and hobbies contain performing the identical actions over and over are sometimes on the best threat of tendinitis. You hear of tennis and golfer’s elbow, jumper’s knee, and swimmer’s shoulder. In all instances, overuse of the joint causes a microtrauma that initiates the inflammatory response. Tendinitis is routinely identified by way of a scientific examination. In case of extreme ache, X-rays may be examined to rule out the opportunity of a bone damage. Extreme instances of tendinitis may even tear unfastened a tendon. Surgical restore of a tendon is painful. Connective tissue within the tendon doesn’t have ample blood provide and heals slowly.
Whereas older adults are in danger for tendinitis as a result of the elasticity of tendon tissue decreases with age, energetic individuals of all ages can develop tendinitis. Younger athletes, dancers, and pc operators; anybody who performs the identical actions continuously is in danger for tendinitis. Though repetitive motions are unavoidable in lots of actions and will result in tendinitis, precautions may be taken that may reduce the chance of growing tendinitis. For energetic people, stretches earlier than exercising and cross coaching or altering workout routines are advisable. For the passionate athlete, it could be time to take some classes to enhance method. All the preventive measures intention to extend the power of the tendon and reduce the stress placed on it. With correct relaxation and managed care, you can be again on the court docket to hit that slice-spin serve over the online.
Supportive Connective Tissues
Two main types of supportive connective tissue, cartilage and bone, enable the physique to keep up its posture and shield inside organs.
Cartilage
The distinctive look of cartilage is because of polysaccharides referred to as chondroitin sulfates, which bind with floor substance proteins to kind proteoglycans. Embedded throughout the cartilage matrix are chondrocytes, or cartilage cells, and the house they occupy are referred to as lacunae (singular = lacuna). A layer of dense irregular connective tissue, the perichondrium, encapsulates the cartilage. Cartilaginous tissue is avascular, thus, all vitamins must diffuse by way of the matrix to achieve the chondrocytes. This can be a issue contributing to the very sluggish therapeutic of cartilaginous tissues.
The three essential forms of cartilage tissue are hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage (Determine 4.3.5 – Forms of Cartilage). Hyaline cartilage, the most typical sort of cartilage within the physique, consists of quick and dispersed collagen fibers and accommodates massive quantities of proteoglycans. Underneath the microscope, tissue samples seem clear. The floor of hyaline cartilage is easy. Each robust and versatile, it’s discovered within the rib cage and nostril and covers bones the place they meet to kind moveable joints. It types the template of the embryonic skeleton earlier than bone formation. A plate of hyaline cartilage on the ends of bone permits continued development till maturity. Fibrocartilage is hard as a result of it has thick bundles of collagen fibers dispersed by way of its matrix. The intervertebral discs are examples of fibrocartilage. Elastic cartilage accommodates elastic fibers in addition to collagen and proteoglycans. This tissue offers help in addition to elasticity. Tug gently at your ear lobes, and spot that the lobes return to their preliminary form. The exterior ear accommodates elastic cartilage.
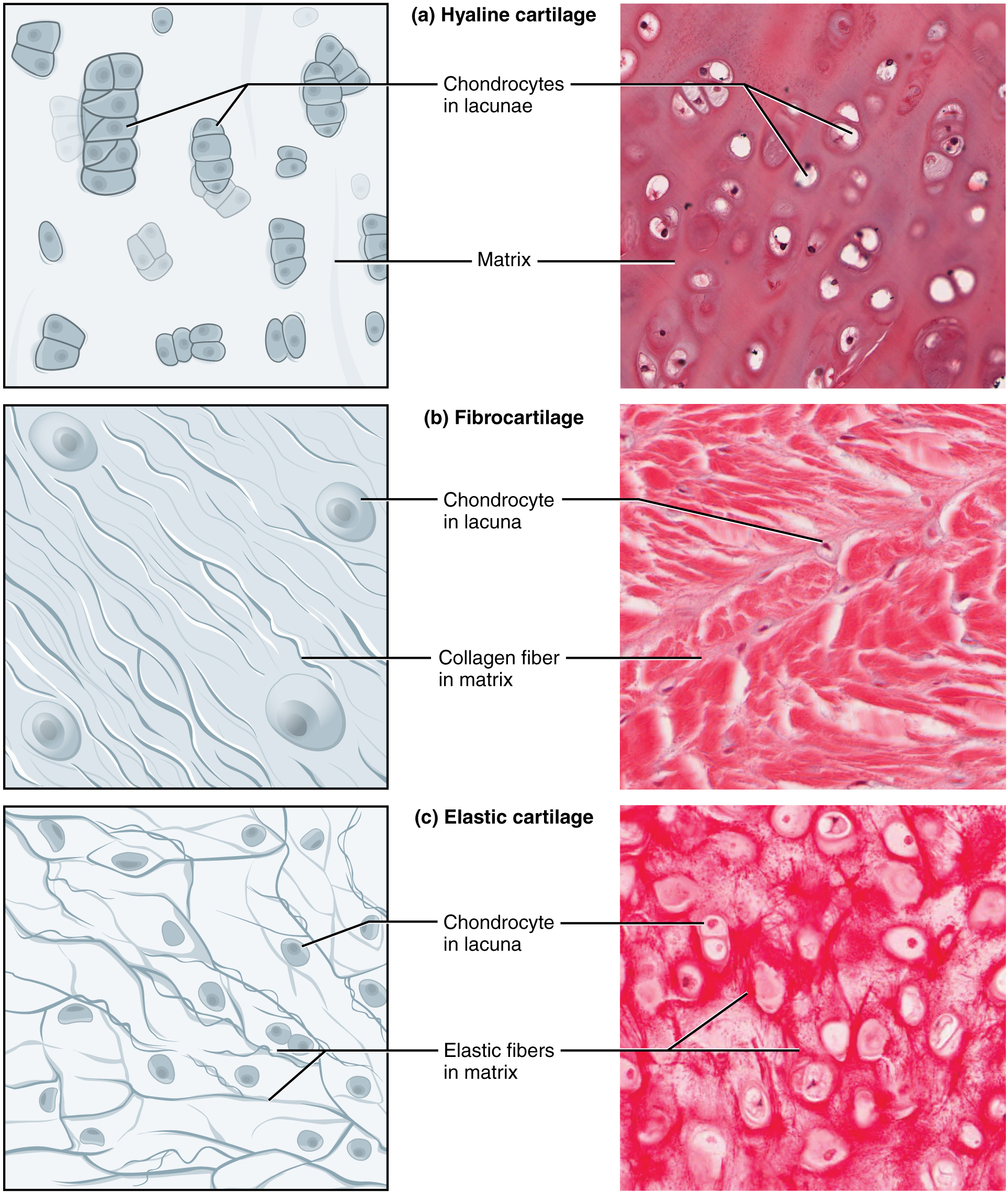
Bone
Bone is the toughest connective tissue. It offers safety to inside organs and helps the physique. Bone’s inflexible extracellular matrix accommodates largely collagen fibers embedded in a mineralized floor substance containing hydroxyapatite, a type of calcium phosphate. Each elements of the matrix, natural and inorganic, contribute to the bizarre properties of bone. With out collagen, bones could be brittle and shatter simply. With out mineral crystals, bones would flex and supply little help. Osteoblasts are the energetic bone forming cells, producing the natural a part of the extracellular matrix. The mature bone cells, osteocytes, are positioned inside lacunae. Bone is a extremely vascularized tissue. Not like cartilage, bone tissue can get better from accidents in a comparatively quick time.
The histology of a cross sectional view of compact bone reveals a typical association of osteocytes in concentric circles round a central canal. This structural unit of compact bone known as the osteon. There is no such thing as a such structural unit in cancellous bone, or spongy bone, which appears like a sponge underneath the microscope and accommodates empty areas between trabeculae. It’s lighter than compact bone and located within the inside of bones and on the finish of lengthy bones. Compact bone is stable and has larger structural power.
Fluid Connective Tissue
Blood and lymph are fluid connective tissues. Cells flow into in a liquid extracellular matrix. The shaped components circulating in blood are all derived from hematopoietic stem cells positioned in bone marrow (Determine 4.3.6 – Blood: A Fluid Connective Tissue). Erythrocytes, purple blood cells, transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Leukocytes, white blood cells, are chargeable for defending in opposition to doubtlessly dangerous microorganisms or molecules. Platelets are cell fragments concerned in blood clotting. Some white blood cells have the flexibility to cross the endothelial layer that strains blood vessels and enter adjoining tissues. Vitamins, salts, and wastes are dissolved within the liquid matrix and transported by way of the physique.
Lymph accommodates a liquid matrix and white blood cells. Lymphatic capillaries are extremely permeable, permitting bigger molecules and extra fluid from interstitial areas to enter the lymphatic vessels. Lymph vessels return molecules and fluid to the venous blood that would not in any other case instantly enter the bloodstream. On this method, specialised lymphatic capillaries transport absorbed fat away from the gut and ship these molecules to the blood.
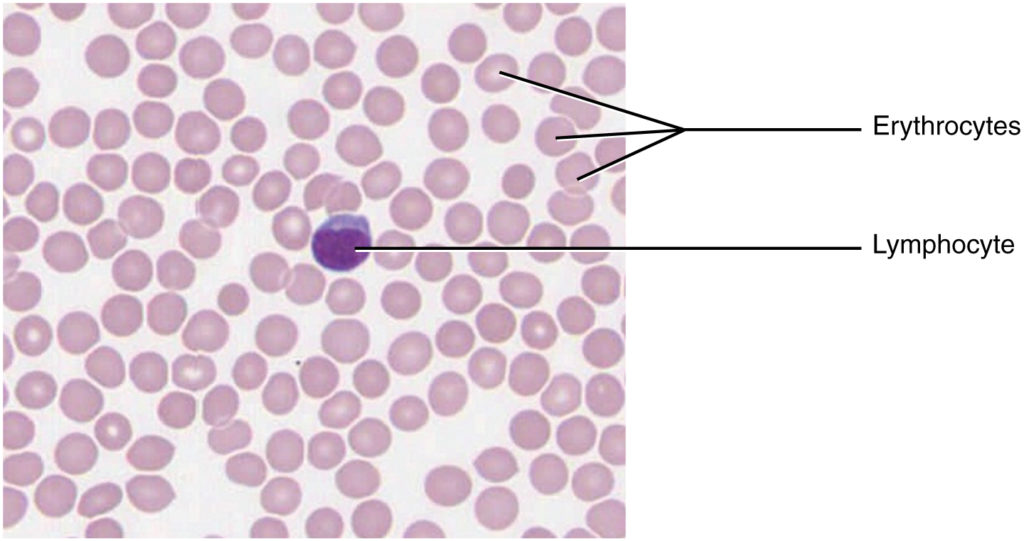
Chapter Assessment
Connective tissue is a heterogeneous tissue with many cell shapes and tissue structure. Structurally, all connective tissues comprise cells which might be embedded in an extracellular matrix stabilized by proteins. The chemical nature and bodily structure of the extracellular matrix and proteins range enormously amongst tissues, reflecting the number of features that connective tissue fulfills within the physique. Connective tissues separate and cushion organs, defending them from shifting or traumatic accidents. Connective tissues additionally present help and help motion, retailer and transport vitality molecules, shield in opposition to infections, and contribute to temperature homeostasis.
Many alternative cells contribute to the formation of connective tissues. They originate within the mesodermal germ layer and differentiate from mesenchyme and hematopoietic tissue within the bone marrow. Fibroblasts are probably the most ample and secrete many protein fibers, adipocytes specialise in fats storage, hematopoietic cells from the bone marrow give rise to all of the blood cells, chondrocytes kind cartilage, and osteocytes kind bone. The extracellular matrix accommodates fluid, proteins, polysaccharide derivatives, and, within the case of bone, mineral crystals. Protein fibers fall into three main teams: collagen fibers (that are thick, robust, versatile, and resist stretch), reticular fibers (that are skinny and kind a supportive mesh, and elastin (fibers which might be skinny and elastic).
The foremost forms of connective tissue are connective tissue correct, supportive tissue, and fluid tissue. Free connective tissue correct consists of adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. These serve to carry organs and different tissues in place and, within the case of adipose tissue, isolate and retailer vitality reserves. The matrix is probably the most ample characteristic for unfastened tissue though adipose tissue doesn’t have a lot extracellular matrix. Dense connective tissue correct is richer in fibers and could also be common, with fibers oriented in parallel as in ligaments and tendons, irregular, with fibers oriented in a number of instructions, or elastic, with a considerable amount of the protein elastin embedded throughout the fibers. Organ capsules (collagenous sort) and partitions of arteries (elastic sort) comprise dense, irregular connective tissue. Cartilage and bone are supportive tissue. Cartilage accommodates chondrocytes and is considerably versatile. Hyaline cartilage is easy and clear, covers joints, and is discovered within the rising portion of bones. Fibrocartilage is hard due to additional collagen fibers and types, amongst different issues, the intervertebral discs. Elastic cartilage can stretch and recoil to its authentic form due to its excessive content material of elastic fibers. Bones are made from a inflexible, mineralized matrix containing calcium salts, crystals, and osteocytes lodged in lacunae. Bone tissue is very vascularized. Cancellous bone is spongy and fewer stable than compact bone. Fluid tissue, for instance blood and lymph, is characterised by a liquid matrix and no supporting fibers.
4.4 Muscle Tissue
Studying Targets
Describe the traits of muscle tissue and the way these dictate muscle operate.
By the top of this part, it is possible for you to to:
- Establish the three forms of muscle tissue
- Evaluate and distinction the features of every muscle tissue sort
Muscle tissue is characterised by properties that enable motion. Muscle cells are excitable; they reply to a stimulus. They’re contractile, that means they will shorten and generate a pulling pressure. When hooked up between two movable objects, corresponding to two bones, contraction of the muscle tissues trigger the bones to maneuver. Some muscle motion is voluntary, which suggests it’s underneath aware management. For instance, an individual decides to open a e-book and skim a chapter on anatomy. Different actions are involuntary, that means they aren’t underneath aware management, such because the contraction of your pupil in vivid mild. Muscle tissue is classed into three sorts based on construction and performance: skeletal, cardiac, and easy (Desk 4.2).
| Muscle sort | Structural components | Operate | Location |
| Skeletal | Lengthy cylindrical fiber, striated, many peripherally positioned nuclei | Voluntary motion, produces warmth, protects organs | Connected to bones and round entry & exit websites of physique (e.g., mouth, anus) |
| Cardiac | Quick, branched, striated, single central nucleus | Contracts to pump blood | Coronary heart |
| Clean | Quick, spindle-shaped, no evident striation, single nucleus in every fiber | Involuntary motion, strikes meals, involuntary management of respiration, strikes secretions, regulates circulation of blood in arteries by contraction | Partitions of main organs and passageways |
Skeletal muscle is hooked up to bones and its contraction makes potential locomotion, facial expressions, posture, and different voluntary actions of the physique. Forty % of your physique mass is made up of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle tissues generate warmth as a byproduct of their contraction and thus take part in thermal homeostasis. Shivering is an involuntary contraction of skeletal muscle tissues in response to decrease than regular physique temperature. The muscle cell, or myocyte, develops from myoblasts derived from the mesoderm. Myocytes and their numbers stay comparatively fixed all through life. Skeletal muscle tissue is organized in bundles surrounded by connective tissue. Underneath the sunshine microscope, muscle cells seem striated with many nuclei squeezed alongside the membranes. The striation is because of the common alternation of the contractile proteins actin and myosin, together with the structural proteins that couple the contractile proteins to connective tissues. The cells are multinucleated because of the fusion of the numerous myoblasts that fuse to kind every lengthy muscle fiber.
Cardiac muscle types the contractile partitions of the center. The cells of cardiac muscle, often called cardiomyocytes, additionally seem striated underneath the microscope. Not like skeletal muscle fibers, cardiomyocytes are single cells with a single centrally positioned nucleus. A principal attribute of cardiomyocytes is that they contract on their very own intrinsic rhythm with out exterior stimulation. Cardiomyocytes connect to 1 one other with specialised cell junctions referred to as intercalated discs. Intercalated discs have each anchoring junctions and hole junctions. Connected cells kind lengthy, branching cardiac muscle fibers that act as a syncytium, permitting the cells to synchronize their actions. The cardiac muscle pumps blood by way of the physique and is underneath involuntary management.
Clean muscle tissue contraction is chargeable for involuntary actions within the inside organs. It types the contractile element of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive programs in addition to the airways and blood vessels. Every cell is spindle formed with a single nucleus and no seen striations (Determine 4.4.1 – Muscle Tissue).
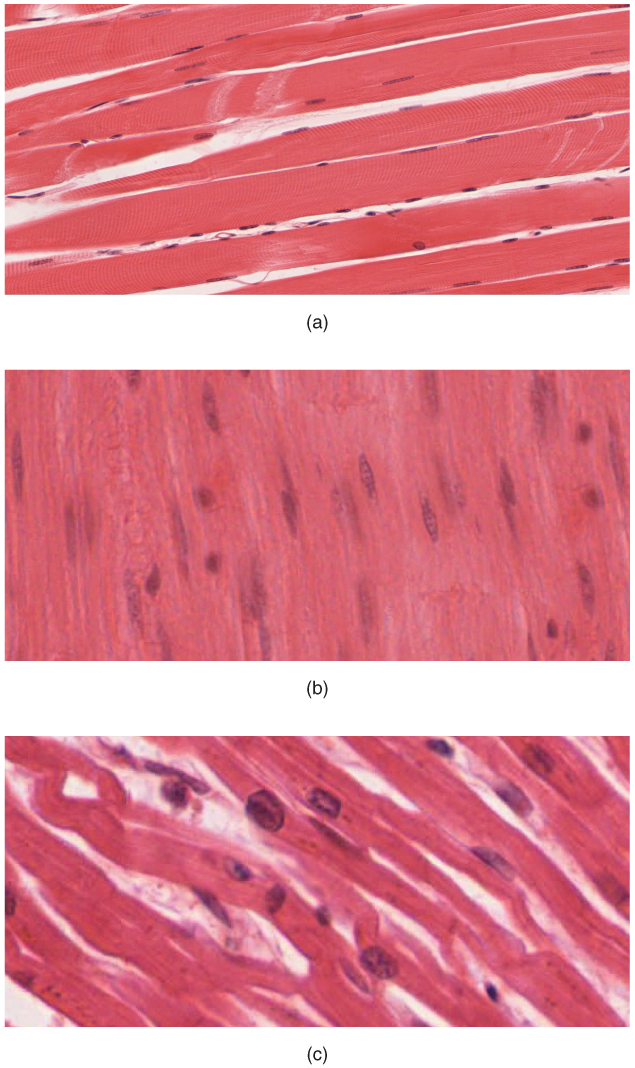
Chapter Assessment
The three forms of muscle cells are skeletal, cardiac, and easy. Their morphologies match their particular features within the physique. Skeletal muscle is voluntary and responds to aware stimuli. The cells are striated and multinucleated showing as lengthy, unbranched cylinders. Cardiac muscle is involuntary and located solely within the coronary heart. Every cell is striated with a single nucleus and so they connect to 1 one other to kind lengthy fibers. Cells are hooked up to 1 one other at intercalated disks. The cells are interconnected bodily and electrochemically to behave as a syncytium. Cardiac muscle cells contract autonomously and involuntarily. Clean muscle is involuntary. Every cell is a spindle-shaped fiber and accommodates a single nucleus. No striations are evident as a result of the actin and myosin filaments don’t align within the cytoplasm.
4.5 Nervous Tissue
Studying Targets
Describe the traits of nervous tissue and the way these allow the distinctive features of nervous tissue.
By the top of this part, it is possible for you to to:
- Establish the courses of cells that make up nervous tissue
- Describe the traits of nervous tissue
Nervous tissue is characterised as being excitable and able to sending and receiving electrochemical alerts that present the physique with data. Two essential courses of cells make up nervous tissue: the neuron and neuroglia (Determine 4.5.1 The Neuron). Neurons propagate data by way of electrochemical impulses, referred to as motion potentials, that are biochemically linked to the discharge of chemical alerts. Neuroglia play a necessary function in supporting neurons.
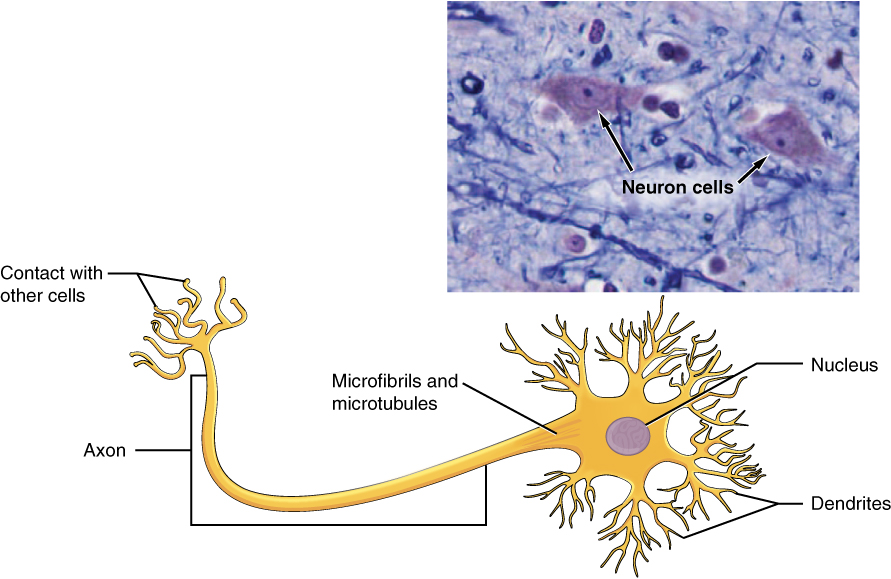
Neurons show distinctive morphology, nicely suited to their function as conducting cells, with three essential components. The cell physique consists of many of the cytoplasm, organelles, and nucleus. Dendrites, which obtain enter from different neurons, department off the cell physique and seem as skinny extensions. An extended axon extends from the cell physique and will be wrapped in an insulating layer often called myelin, which is shaped by accent cells. Axons transmit electrical alerts touring away from the cell physique. The synapse is the hole between nerve cells, or between a nerve cell and its goal. The sign is transmitted throughout the synapse by chemical compounds often called neurotransmitters. Neurons categorized as multipolar neurons have a number of dendrites and a single distinguished axon. Bipolar neurons possess a single dendrite and axon with the cell physique, whereas unipolar neurons have solely a single course of extending out from the cell physique, which divides right into a useful dendrite and right into a useful axon. When a neuron is sufficiently stimulated, it generates an motion potential that propagates down the axon in the direction of the synapse. If sufficient neurotransmitters are launched on the synapse to stimulate the subsequent neuron (or muscle, or gland), a response is generated.
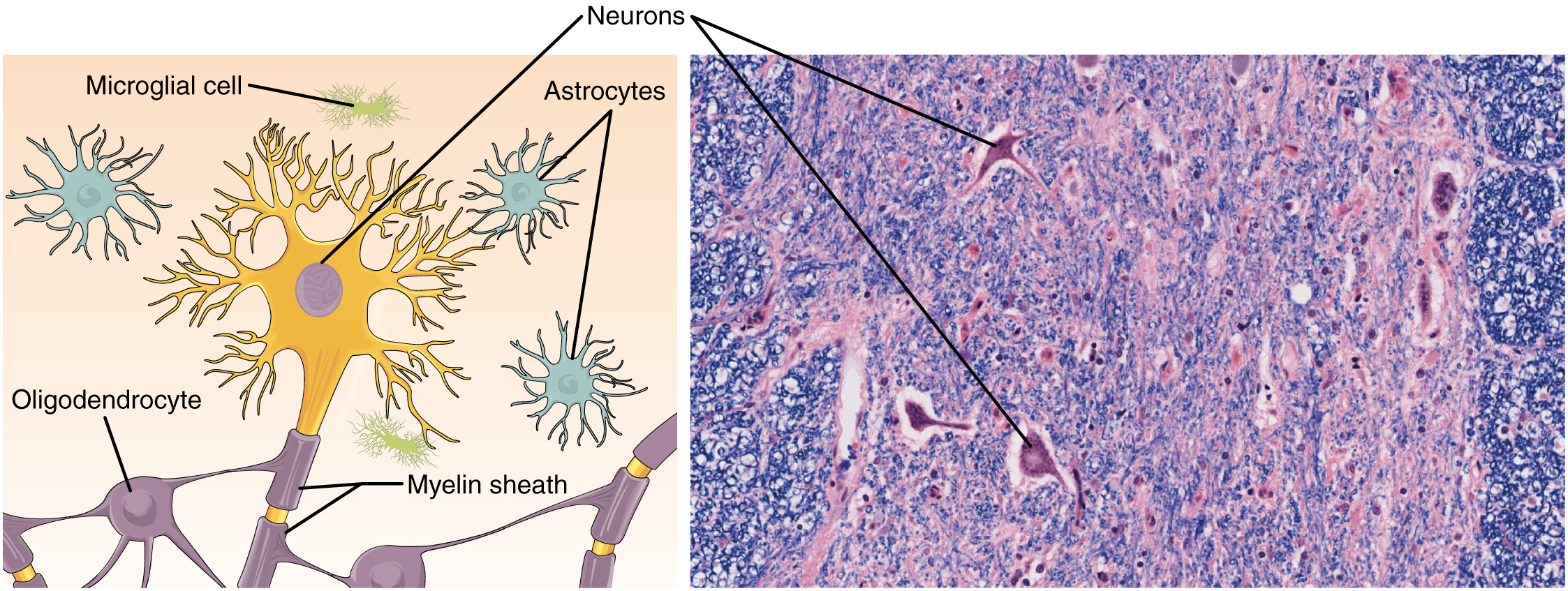
The second class of neural cells are the neuroglia or glial cells, which have been characterised as having a easy help function. The phrase “glia” comes from the Greek phrase for glue. Latest analysis is shedding mild on the extra advanced function of neuroglia within the operate of the mind and nervous system. Astrocyte cells, named for his or her distinctive star form, are ample within the central nervous system. The astrocytes have many features, together with regulation of ion focus within the intercellular house, uptake and/or breakdown of some neurotransmitters, and formation of the blood-brain barrier, the membrane that separates the circulatory system from the mind. Microglia shield the nervous system in opposition to an infection and are associated to macrophages. Oligodendrocyte cells produce myelin within the central nervous system (mind and spinal wire) whereas the Schwann cell produces myelin within the peripheral nervous system (Figure 4.5.2 Nervous Tissue).
Chapter Assessment
Essentially the most distinguished cell of the nervous tissue, the neuron, is characterised primarily by its means to obtain stimuli and reply by producing {an electrical} sign, often called an motion potential, which may journey quickly over nice distances within the physique. A typical neuron shows a particular morphology: a big cell physique branches out into quick extensions referred to as dendrites, which obtain chemical alerts from different neurons, and an extended tail referred to as an axon, which relays alerts away from the cell to different neurons, muscle tissues, or glands. Many axons are wrapped by a myelin sheath, a lipid by-product that acts as an insulator and facilitates the transmission of the motion potential. Different cells within the nervous tissue, the neuroglia, embody the astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells.
4.6 Tissue Damage and Ageing
Studying Targets
Describe the method of tissue response to damage.
By the top of this part, it is possible for you to to:
- Establish the cardinal indicators of irritation
- Listing the physique’s response to tissue damage
- Clarify the method of tissue restore
- Talk about the progressive influence of getting older on tissue
- Describe cancerous mutations’ impact on tissue
Tissues of every type are weak to damage and, inevitably, getting older. Within the former case, understanding how tissues reply to wreck can information methods to assist restore. Within the latter case, understanding the influence of getting older can assist within the seek for methods to decrease its results.
Tissue Damage and Restore
Irritation is the usual, preliminary response of the physique to damage. Whether or not organic, chemical, bodily, or radiation burns, all accidents result in the identical sequence of physiological occasions. Irritation limits the extent of damage, partially or totally eliminates the reason for damage, and initiates restore and regeneration of broken tissue. Necrosis, or unintended cell dying, causes irritation. Apoptosis is programmed cell dying, a standard step-by-step course of that destroys cells not wanted by the physique. By mechanisms nonetheless underneath investigation, apoptosis doesn’t provoke the inflammatory response. Acute irritation resolves over time by the therapeutic of tissue. If irritation persists, it turns into persistent and results in diseased situations. Arthritis and tuberculosis are examples of persistent irritation. The suffix “-itis” denotes irritation of a particular organ or sort. For instance, peritonitis is the irritation of the peritoneum, and meningitis refers back to the irritation of the meninges, the robust membranes that encompass the central nervous system.
The 4 cardinal indicators of irritation—redness (not less than for individuals with mild coloured pores and skin), swelling, ache, and native warmth—have been first recorded in antiquity. Cornelius Celsus is credited with documenting these indicators through the days of the Roman Empire, as early as the primary century AD. A fifth signal, lack of operate, may accompany irritation.
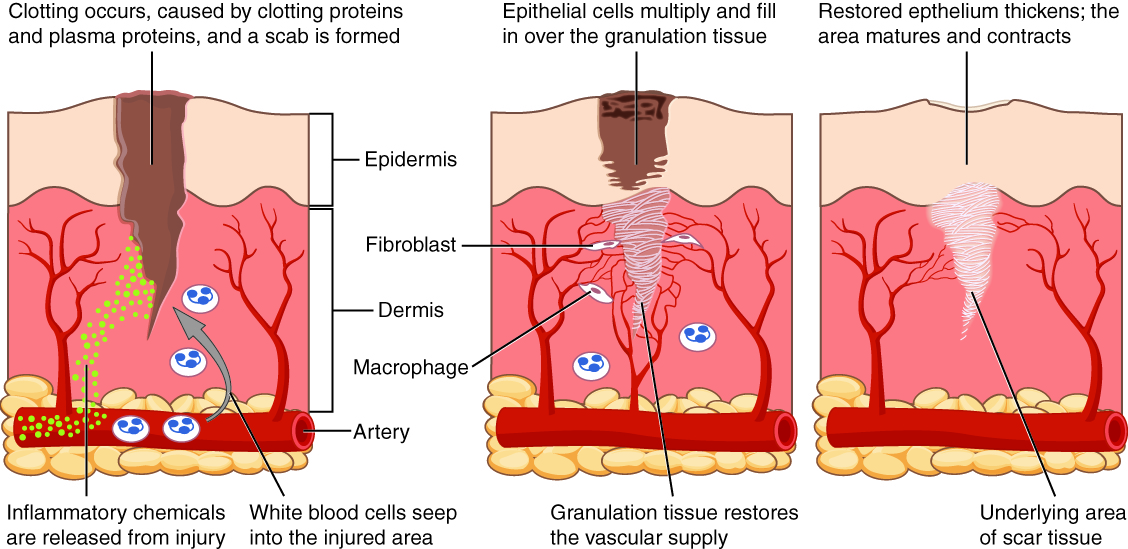
Upon tissue damage, broken cells launch inflammatory chemical alerts that evoke native vasodilation, the widening of the blood vessels. Elevated blood circulation can change the colour of the integument and end in a localized temperature enhance. In response to damage, mast cells current in tissue degranulate, releasing the potent vasodilator histamine. Elevated blood circulation and inflammatory mediators recruit white blood cells to the location of irritation. The endothelium lining the native blood vessel turns into “leaky” underneath the affect of histamine and different inflammatory mediators permitting neutrophils, macrophages, and fluid to maneuver from the blood into the interstitial tissue areas. The surplus liquid in tissue causes swelling, correctly referred to as edema. The swollen tissues stimulate mechanical receptors, which may trigger the notion of ache. Prostaglandins launched from injured cells additionally activate ache pathways. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs) cut back perceived ache as a result of they inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins. Excessive ranges of NSAIDs cut back irritation. Antihistamines lower allergy symptoms by blocking histamine receptors and consequently, the histamine response.
After containment of an damage, the tissue restore section begins with removing of poisons and waste merchandise. Clotting (coagulation) reduces blood loss from broken blood vessels and types a community of fibrin proteins that lure blood cells and bind the sides of the wound collectively. A scab types when the clot dries, decreasing the danger of an infection. Typically a combination of useless leukocytes and fluid referred to as pus accumulates within the wound. As therapeutic progresses, fibroblasts from the encompassing connective tissues change the collagen and extracellular materials misplaced by the damage. Angiogenesis, the expansion of recent blood vessels, leads to vascularization of the brand new tissue often called granulation tissue. The clot retracts pulling the sides of the wound collectively, and it slowly dissolves because the tissue is repaired. When a considerable amount of granulation tissue types and capillaries disappear, a pale scar is commonly seen within the healed space. A main union describes the therapeutic of a wound the place the sides are shut collectively. When there’s a gaping wound, it takes longer to refill the world with cells and collagen. The method referred to as secondary union happens as the sides of the wound are pulled collectively by what known as wound contraction. When a wound is multiple quarter of an inch deep, sutures (stitches) are advisable to advertise a main union and keep away from the formation of a disfiguring scar. Regeneration is the addition of recent cells of the identical sort as those that have been injured (Determine 4.6.1 – Tissue Therapeutic).
Tissue and Ageing
In line with poet Ralph Waldo Emerson, “The surest poison is time.” Actually, biology confirms that many features of the physique decline with age. All of the cells, tissues, and organs are affected by senescence, with noticeable variability between people owing to totally different genetic make-up and life. The outward indicators of getting older are simply recognizable. The pores and skin and different tissues change into thinner and drier, decreasing their elasticity, contributing to wrinkles and hypertension. Hair turns grey as a result of follicles produce much less melanin, the brown pigment of hair and the iris of the attention. The face appears flabby as a result of elastic and collagen fibers lower in connective tissue and muscle tone is misplaced. Glasses and listening to aids could change into components of life because the senses slowly deteriorate, all as a result of lowered elasticity. Total top decreases because the bones lose calcium and different minerals. With age, fluid decreases within the fibrous cartilage disks intercalated between the vertebrae within the backbone. Joints lose cartilage and stiffen. Many tissues, together with these in muscle tissues, lose mass by way of a course of referred to as atrophy. Lumps and rigidity change into extra widespread. As a consequence, the passageways, blood vessels, and airways change into extra inflexible. The mind and spinal wire lose mass. Nerves don’t transmit impulses with the identical velocity and frequency as previously. Some lack of thought, readability, and reminiscence can accompany getting older. Extra extreme issues should not essentially related to the getting older course of and could also be signs of an underlying sickness.
As exterior indicators of getting older enhance, so do the inside indicators, which aren’t as noticeable. The incidence of coronary heart illnesses, respiratory syndromes, and kind 2 diabetes will increase with age, although these should not essentially age-dependent results. Wound therapeutic is slower within the aged, accompanied by the next frequency of an infection because the capability of the immune system to fend off pathogens declines.
Ageing can also be obvious on the mobile stage as a result of all cells expertise adjustments with getting older. Telomeres, areas of the chromosomes needed for cell division, shorten every time cells divide. As they do, cells are much less in a position to divide and regenerate. Due to alterations in cell membranes, transport of oxygen and vitamins into the cell and removing of carbon dioxide and waste merchandise from the cell should not as environment friendly within the aged. Cells could start to operate abnormally, which can result in illnesses related to getting older, together with arthritis, reminiscence points, and a few cancers.
The progressive influence of getting older on the physique varies significantly amongst people. Nonetheless, research point out that train and wholesome way of life decisions can decelerate the deterioration of the physique that comes with previous age.
Homeostatic Imbalances: Tissues and Most cancers
Most cancers is a generic time period for a lot of illnesses through which cells escape regulatory alerts. Uncontrolled development, invasion into adjoining tissues, and colonization of different organs, if not handled early sufficient, are its hallmarks. Well being suffers when tumors “rob” blood provide from the “regular” organs.
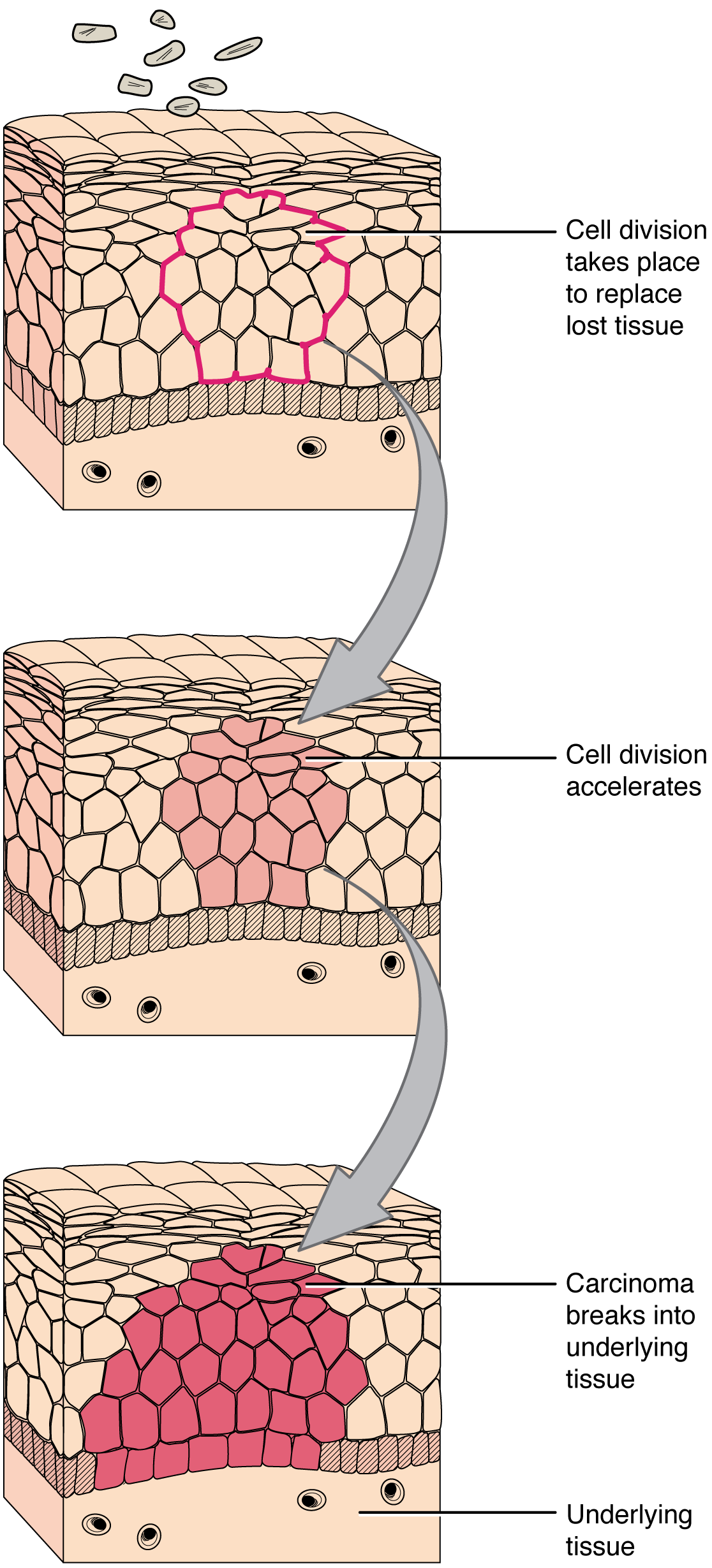
A mutation is outlined as a everlasting change within the DNA of a cell. Epigenetic modifications, adjustments that don’t have an effect on the code of the DNA however alter how the DNA is decoded, are additionally identified to generate irregular cells. Alterations within the genetic materials could also be attributable to environmental brokers, infectious brokers, or errors within the replication of DNA that accumulate with age. Many mutations don’t trigger any noticeable change within the features of a cell, nonetheless, if the modification impacts key proteins that have an effect on the cell’s means to proliferate in an orderly vogue, the cell begins to divide abnormally. As adjustments in cells accumulate, they lose their means to kind common tissues. A tumor, a mass of cells displaying irregular structure, types within the tissue. Many tumors are benign, that means they don’t metastasize nor trigger illness. A tumor turns into malignant, or cancerous, when it breaches the confines of its tissue, promotes angiogenesis, attracts the expansion of capillaries, and metastasizes to different organs (Determine 4.6.2 Improvement of Most cancers). The particular names of cancers replicate the tissue of origin. Cancers derived from epithelial cells are known as carcinomas. Most cancers in myeloid tissue or blood cells kind myelomas. Leukemias are cancers of white blood cells, whereas sarcomas derive from connective tissue. Cells in tumors differ each in construction and performance. Some cells, referred to as most cancers stem cells, look like a subtype of cell chargeable for uncontrolled development. Latest analysis reveals that opposite to what was beforehand assumed, tumors should not disorganized plenty of cells, however have their very own buildings.
Most cancers remedies range relying on the illness’s sort and stage. Conventional approaches, together with surgical procedure, radiation, chemotherapy, and hormonal remedy. The intention is to take away or kill quickly dividing most cancers cells, however these methods have their limitations. Relying on a tumor’s location, for instance, most cancers surgeons could also be unable to take away it. Radiation and chemotherapy are troublesome, and it’s typically not possible to focus on solely the most cancers cells. The remedies inevitably destroy wholesome tissue as nicely. To deal with this, researchers are engaged on prescribed drugs that may goal particular proteins implicated in cancer-associated molecular pathways.
Chapter Assessment
Irritation is the basic response of the physique to damage and follows a typical sequence of occasions. The world is purple, feels heat to the contact, swells, and is painful. Injured cells, mast cells, and resident macrophages launch chemical alerts that trigger vasodilation and fluid leakage within the surrounding tissue. The restore section consists of blood clotting, adopted by regeneration of tissue as fibroblasts deposit collagen. Some tissues regenerate extra readily than others. Epithelial and connective tissues change broken or useless cells from a provide of grownup stem cells. Muscle and nervous tissues bear both sluggish regeneration or don’t restore in any respect.
Age impacts all of the tissues and organs of the physique. Broken cells don’t regenerate as quickly as in youthful individuals. Notion of sensation and effectiveness of response are misplaced within the nervous system. Muscle groups atrophy, and bones lose mass and change into brittle. Collagen decreases in some connective tissue, and joints stiffen.